Page 333 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 333
323 radar, airborne-early-warning (AEW) radar, airborne mapping
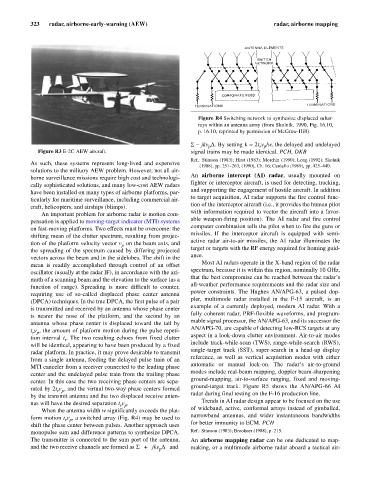
Figure R4 Switching network to synthesize displaced subar-
rays within an antenna array (from Skolnik, 1990, Fig. 16.10,
p. 16.10, reprinted by permission of McGraw-Hill).
jk
v
S - D. By setting k » 2t v /w, the delayed and undelayed
p r p
Figure R3 E-2C AEW aircraft. signal trains may be made identical. PCH, DKB
Ref.: Stimson (1983); Hirst (1983); Morchin (1990); Long (1992); Skolnik
As such, these systems represent long-lived and expensive
(1988), pp. 251–263, (1990), Ch. 16; Cantafio (1989), pp. 425–440.
solutions to the military AEW problem. However, not all air-
An airborne intercept (AI) radar, usually mounted on
borne surveillance missions require high cost and technologi-
fighter or interceptor aircraft, is used for detecting, tracking,
cally sophisticated solutions, and many low-cost AEW radars
and supporting the engagement of hostile aircraft. In addition
have been installed on many types of airborne platforms, par-
to target acquisition, AI radar supports the fire control func-
ticularly for maritime surveillance, including commercial air-
tion of the interceptor aircraft (i.e., it provides the human pilot
craft, helicopters, and airships (blimps).
with information required to vector the aircraft into a favor-
An important problem for airborne radar is motion com-
able weapon-firing position). The AI radar and fire control
pensation is applied to moving-target indicator (MTI) systems
computer combination tells the pilot when to fire the guns or
on fast-moving platforms. Two effects must be overcome: the
missiles. If the interceptor aircraft is equipped with semi-
shifting mean of the clutter spectrum, resulting from projec-
active radar air-to-air missiles, the AI radar illuminates the
tion of the platform velocity vector v on the beam axis, and
p
the spreading of the spectrum caused by differing projected target or targets with the RF energy required for homing guid-
ance.
vectors across the beam and in the sidelobes. The shift in the
Most AI radars operate in the X-band region of the radar
mean is readily accomplished through control of an offset
spectrum, because it is within this region, nominally 10 GHz,
oscillator (usually at the radar IF), in accordance with the azi-
that the best compromise can be reached between the radar’s
muth of a scanning beam and the elevation to the surface (as a
all-weather performance requirements and the radar size and
function of range). Spreading is more difficult to counter,
power constraints. The Hughes AN/APG-63, a pulsed dop-
requiring use of so-called displaced phase center antenna
pler, multimode radar installed in the F-15 aircraft, is an
(DPCA) techniques. In the true DPCA, the first pulse of a pair
example of a currently deployed, modern AI radar. With a
is transmitted and received by an antenna whose phase center
fully coherent radar, PRF-flexible waveforms, and program-
is nearer the nose of the platform, and the second by an
mable signal processor, the AN/APG-63, and its successor the
antenna whose phase center is displaced toward the tail by
AN/APG-70, are capable of detecting low-RCS targets at any
t v , the amount of platform motion during the pulse repeti-
r p
tion interval t . The two resulting echoes from fixed clutter aspect in a look-down clutter environment. Air-to-air modes
r
will be identical, appearing to have been produced by a fixed include track-while-scan (TWS), range-while-search (RWS),
single-target track (SST), super-search in a head-up display
radar platform. In practice, it may prove desirable to transmit
reference, as well as vertical acquisition modes with either
from a single antenna, feeding the delayed pulse train of an
automatic or manual lock-on. The radar’s air-to-ground
MTI canceler from a receiver connected to the leading phase
modes include real-beam mapping, doppler beam-sharpening
center and the undelayed pulse train from the trailing phase
ground-mapping, air-to-surface ranging, fixed and moving-
center. In this case the two receiving phase centers are sepa-
ground-target track. Figure R5 shows the AN/APG-66 AI
rated by 2t v , and the virtual two-way phase centers formed
r p
by the transmit antenna and the two displaced receive anten- radar during final testing on the F-16 production line.
Trends in AI radar design appear to be focused on the use
nas will have the desired separation t v .
r p
When the antenna width w significantly exceeds the plat- of wideband, active, conformal arrays instead of gimballed,
narrowband antennas, and wider instantaneous bandwidths
form motion t v , a switched array (Fig. R4) may be used to
r p
shift the phase center between pulses. Another approach uses for better immunity to ECM. PCH
monopulse sum and difference patterns to synthesize DPCA. Ref.: Stimson (1983); Brookner (1988), p. 215.
The transmitter is connected to the sum port of the antenna, An airborne mapping radar can be one dedicated to map-
and the two receive channels are formed as S + jkv D and making, or a multimode airborne radar aboard a tactical air-
p