Page 47 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 47
antenna radiation regions antenna, reflector 37
Reactive y
near-field Radiating
region
far-field
region r, q,f
x,y,z
r
r'
Antenna q
x
h z
f
Radiating
near-field w
region
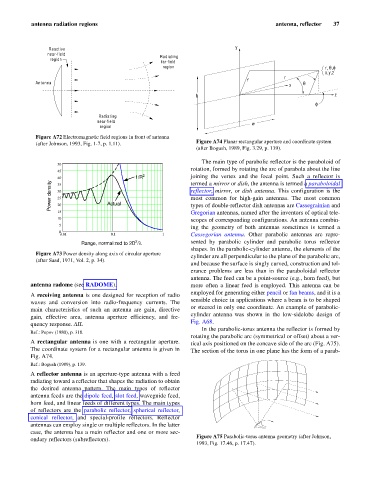
Figure A72 Electromagnetic field regions in front of antenna
Figure A74 Planar rectangular aperture and coordinate system
(after Johnson, 1993, Fig. 1-7, p. 1.11).
(after Bogush, 1989, Fig. 3.29, p. 139).
The main type of parabolic reflector is the paraboloid of
50
rotation, formed by rotating the arc of parabola about the line
45
40 1/R 2 joining the vertex and the focal point. Such a reflector is
Power density 30 Actual reflector, mirror, or dish antenna. This configuration is the
termed a mirror or dish, the antenna is termed a paraboloidal
35
most common for high-gain antennas. The most common
25
20
15 types of double-reflector dish antennas are Cassegrainian and
Gregorian antennas, named after the inventors of optical tele-
10
scopes of corresponding configurations. An antenna combin-
5
ing the geometry of both antennas sometimes is termed a
0
0.01 0.1 1 Cassegorian antenna. Other parabolic antennas are repre-
2
Range, normalized to 2D /l sented by parabolic cylinder and parabolic torus reflector
shapes. In the parabolic-cylinder antenna, the elements of the
Figure A73 Power density along axis of circular aperture
cylinder are all perpendicular to the plane of the parabolic arc,
(after Saad, 1971, Vol. 2, p. 34).
and because the surface is singly curved, construction and tol-
erance problems are less than in the paraboloidal reflector
antenna. The feed can be a point-source (e.g., horn feed), but
antenna radome (see RADOME). more often a linear feed is employed. This antenna can be
employed for generating either pencil or fan beams, and it is a
A receiving antenna is one designed for reception of radio
sensible choice in applications where a beam is to be shaped
waves and conversion into radio-frequency currents. The
or steered in only one coordinate. An example of parabolic-
main characteristics of such an antenna are gain, directive
cylinder antenna was shown in the low-sidelobe design of
gain, effective area, antenna aperture efficiency, and fre-
Fig. A68.
quency response. AIL
In the parabolic-torus antenna the reflector is formed by
Ref.: Popov (1980), p. 318.
rotating the parabolic arc (symmetrical or offset) about a ver-
A rectangular antenna is one with a rectangular aperture. tical axis positioned on the concave side of the arc (Fig. A75).
The coordinate system for a rectangular antenna is given in The section of the torus in one plane has the form of a parab-
Fig. A74.
Ref.: Bogush (1989), p. 139.
A reflector antenna is an aperture-type antenna with a feed
radiating toward a reflector that shapes the radiation to obtain
the desired antenna pattern. The main types of reflector
antenna feeds are the dipole feed, slot feed, waveguide feed,
horn feed, and linear feeds of different types. The main types
of reflectors are the parabolic reflector, spherical reflector,
conical reflector, and special-profile reflectors. Reflector
antennas can employ single or multiple reflectors. In the latter
case, the antenna has a main reflector and one or more sec-
Figure A75 Parabolic-torus antenna geometry (after Johnson,
ondary reflectors (subreflectors).
1993, Fig. 17.46, p. 17.47).