Page 232 - Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry
P. 232
216 Radiochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry
crystal adjusts itself during the drifting process so that the lithium atoms compensate the
impurities. This is, however, not a stable situation when the drifting operation is stopped.
Hence, the final state is "frozen" by cooling of the drifted crystal to liquid nitrogen
temperature. Accidental heat-up will destroy the lithium compensation and the detector must
be redrifled.
When a potential is applied over such a crystal, with the positive terminal at the high
lithium side, three volumes are created, one of p-type, a middle "intrinsic" one, and an
n-type one (p-i-n detectors). In the intrinsic volume the lithium donor electrons neutralize
any original impurities, which are of acceptor p-type. The intrinsic volume becomes
depleted and thereby sensitive to nuclear radiation, and detectors with depleted volumes up
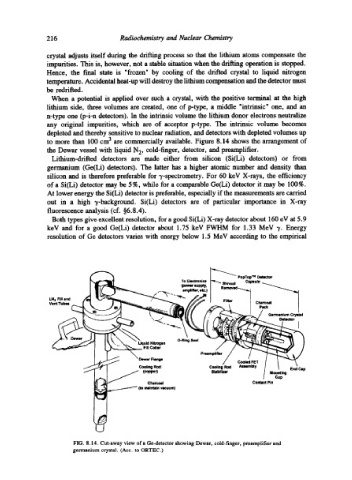
to more than 100 cm 3 are commercially available. Figure 8.14 shows the arrangement of
the Dewar vessel with liquid N 2, cold-finger, detector, and preamplifier.
Lithium-drifted detectors are made either from silicon (Si(Li) detectors) or from
germanium (Ge(Li) detectors). The latter has a higher atomic number and density than
silicon and is therefore preferable for "y-spectrometry. For 60 keV X-rays, the efficiency
of a Si(Li) detector may be 5 %, while for a comparable Ge(Li) detector it may be 100%.
At lower energy the $i(Li) detector is preferable, especially if the measurements are carried
out in a high "),-background. Si(Li) detectors are of particular importance in X-ray
fluorescence analysis (of. w
Both types give excellent resolution, for a good Si(Li) X-ray detector about 160 eV at 5.9
keV and for a good Ge(Li) detector about 1.75 keV FWHM for 1.33 MeV ~. Energy
resolution of Ge detectors varies with energy below 1.5 MeV according to the empirical
PopTop TM Doqlsctor
To Electronics Capsule
(power supply, ~'q'~ Shroud
amplifier, eta:.)
LN 2 Fill lind Filter
Vent Tubes C
Pick ]
Germanium Crystal
O-Ring Seal
LkluM Nitrogen
Fill Collar
Preamplifier
Flange
/ Cooled FET
Cooling Rod Cooling Rod Assembly End Cap
'(copper) Stabilizer / Mounting
/ Cup
Charcoal Contact Pin
(to maintain vacuum)
FIG. 8.14. Cut-away view of a Ge-detector showing Dewar, cold-finger, preamplifier and
germanium crystal. (Acc. to ORTEC.)