Page 93 - Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry
P. 93
82 Radiochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry
100001 , ,
'1
Total activity
lO0O
>.
I"
>
a,m
I.-
I
I Longdived component
(halfdife 24 hours)
I
looi: I
I
I
l Short-lived component
(half-Me 4 hours)
',,-I
I
10 J I I I I II I I I I I I
0 5 10152025303540455055606570
TIME (hours)
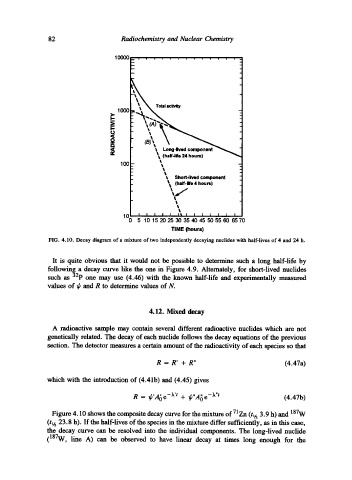
FIG. 4.10. Decay diagram of a mixture of two independently decaying nuclides with half-lives of 4 and 24 h.
It is quite obvious that it would not be possible to determine such a long half-life by
following a decay curve like the one in Figure 4.9. Alternately, for short-lived nuclides
such as 32p one may use (4.46) with the known half-life and experimentally measured
values of ~/, and R to determine values of N.
4.12. Mixed decay
A radioactive sample may contain several different radioactive nuclides which are not
genetically related. The decay of each nuclide follows the decay equations of the previous
section. The detector measures a certain amount of the radioactivity of each species so that
R = R' + R" (4.47a)
which with the introduction of (4.41b) and (4.45) gives
R = r e-X't + r +-X'~ (4.47b)
Figure 4.10 shows the composite decay curve for the mixture of 71Zn (tt h 3.9 h) and 187W
(h h 23.8 h). If the half-lives of the species in the mixture differ sufficiently, as in this case,
the decay curve can be resolved into the individual components. The long-lived nuclide
(187W, line A) can be observed to have linear decay at times long enough for the