Page 325 - Reciprocating Compressors Operation Maintenance
P. 325
3 f O Reciprocating Compressors: Operation and Maintenance
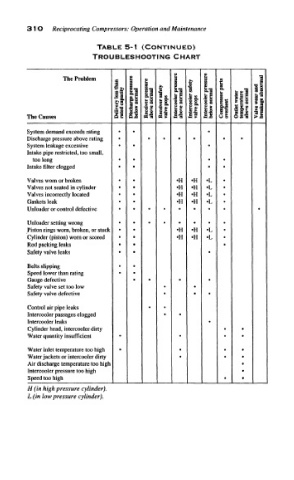
TABLE 5-1 (CONTINUED)
TROUBLESHOOTING CHART
t
The Problem i £ i
!*• !_, ll i,"" 1 al I, i I i
u 1
Ag
1.1
11 |s |g Ss| is it fe 1 b «B § P &t a
58
mSm
£•* ii ii fig _
I! li li ii liii ii If III
The Causes
System demand exceeds rating * * * * *
Discharge pressure above rating * • • * •
System leakage excessive * * «
Intake pipe restricted, too small,
too long • * * *
Intake filter clogged • • • *
Valves worn or broken . . •H •H •L .
Valves not seated in cylinder * * •H •H •L *
Valves incorrectly located * • •H •H •L *
Gaskets leak * • •H *H •L •
Unloader or control defective •
Unloader setting wrong . . . * * * . .
Piston rings worn, broken, or stuck * * •H •H •L *
Cylinder (piston) worn or scored • • •H •H •L *
Rod packing leaks * • •
Safely valve leaks * * *
Belts slipping . .
Speed lower than rating « •
Gauge defective • * • •
Safety valve set too low * •
Safety valve defective * • *
Control air pipe leaks . *
Intercooler passages clogged * •
Intercooler leaks •
Cylinder head, intercooler dirty • .
Water quantity insufficient • • * *
Water inlet temperature too high * . . .
Water jackets or intercooler dirty * * *
Air discharge temperature too high *
Intercooler pressure too high •
Speed too high • *
H (in high pressure cylinder).
L (in low pressure cylinder).