Page 88 - Reciprocating Compressors Operation Maintenance
P. 88
Design and Mate rials for Reciprocating Compressor Components 7 5
The rider ring is either a solid or a split configuration; its size is deter-
mined by piston assembly weight only and is independent of operating
pressures.
CONVENTIONAL DESIGN FOR NON-LUBE SERVICE
It should be obvious that the non-lube cylinder is not a mere factory
conversion of a lubricated cylinder. Simply changing out the piston rings
and packing rings from metallic to carbon or teflon and shutting off the
lubricating oil does not make a non-lube cylinder. Successful operation
means that the non-lube cylinder must be engineered for non-lube ser-
vice, using materials developed and thoroughly tested for this service.
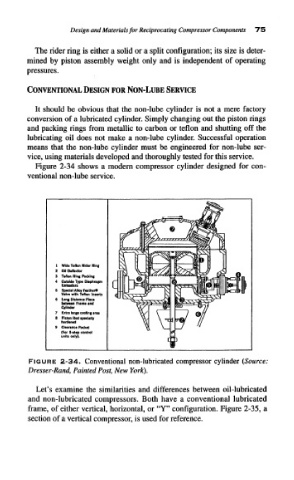
Figure 2-34 shows a modern compressor cylinder designed for con-
ventional non-lube service.
4
Untotders
6 Special Alloy Fe»lher»
VMw with Teflon Inserts
6 Long Distance Piece
batmen Fnnra md
Cylinder
7 Erin Urge cooling area
8 Piiton Rod specially
fiardmtd
9 Clearance Pocket
(For 5 «tep control
unHi only).
FIGURE 2-34. Conventional non-lubricated compressor cylinder (Source:
Dresser-Rand, Painted Post, New York).
Let's examine the similarities and differences between oil-lubricated
and non-lubricated compressors. Both have a conventional lubricated
frame, of either vertical, horizontal, or "Y" configuration. Figure 2-35, a
section of a vertical compressor, is used for reference.