Page 180 - Reliability and Maintainability of In service Pipelines
P. 180
164 Reliability and Maintainability of In-Service Pipelines
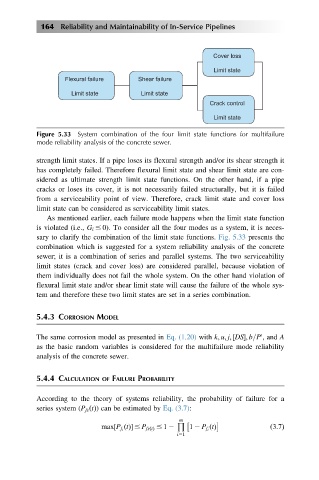
Cover loss
Limit state
Flexural failure Shear failure
Limit state Limit state
Crack control
Limit state
Figure 5.33 System combination of the four limit state functions for multifailure
mode reliability analysis of the concrete sewer.
strength limit states. If a pipe loses its flexural strength and/or its shear strength it
has completely failed. Therefore flexural limit state and shear limit state are con-
sidered as ultimate strength limit state functions. On the other hand, if a pipe
cracks or loses its cover, it is not necessarily failed structurally, but it is failed
from a serviceability point of view. Therefore, crack limit state and cover loss
limit state can be considered as serviceability limit states.
As mentioned earlier, each failure mode happens when the limit state function
is violated (i.e., G i # 0). To consider all the four modes as a system, it is neces-
sary to clarify the combination of the limit state functions. Fig. 5.33 presents the
combination which is suggested for a system reliability analysis of the concrete
sewer; it is a combination of series and parallel systems. The two serviceability
limit states (crack and cover loss) are considered parallel, because violation of
them individually does not fail the whole system. On the other hand violation of
flexural limit state and/or shear limit state will cause the failure of the whole sys-
tem and therefore these two limit states are set in a series combination.
5.4.3 CORROSION MODEL
The same corrosion model as presented in Eq. (1.20) with k; u; j; ½DS; b=P ; and A
0
as the basic random variables is considered for the multifailure mode reliability
analysis of the concrete sewer.
5.4.4 CALCULATION OF FAILURE PROBABILITY
According to the theory of systems reliability, the probability of failure for a
series system (P fs ðtÞ) can be estimated by Eq. (3.7):
m
t ðÞ ð3:7Þ
max½P f i t ðÞ # P fs tðÞ # 1 2 L 1 2 P f i
i51