Page 112 - Renewable Energy Devices and System with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS
P. 112
Overview of PV Maximum Power Point Tracking Techniques 99
the current and voltage in the single-diode model of the PV modules. The resulting value is used to
detect whether a variation of the PV source output power is due to a change of the solar irradiation
conditions or the MPPT process itself.
The P&O method is characterized by its operational and implementation simplicity. However, it
exhibits a slow convergence speed under varying solar irradiation conditions and its performance
may also be affected by system noise.
5.3.3 Incremental-Conductance MPPT
At the MPP of the PV source, it holds that
⋅ )
=⇒ = I pv + V pv =⇒ =−
∂P pv ∂(I pv V pv ∂I pv ∂I pv I pv (5.6)
0
0
∂V pv ∂V pv ∂V pv ∂V pv V ppv
where I pv is the output current of the PV array.
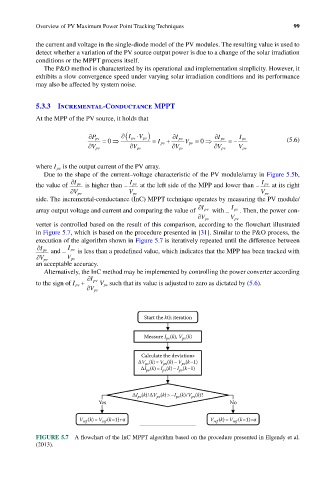
Due to the shape of the current–voltage characteristic of the PV module/array in Figure 5.5b,
the value of ∂I pv is higher than − I pv at the left side of the MPP and lower than − I pv at its right
∂V pv V pv V pv
side. The incremental-conductance (InC) MPPT technique operates by measuring the PV module/
array output voltage and current and comparing the value of ∂I pv with − I pv . Then, the power con-
∂V pv V pv
verter is controlled based on the result of this comparison, according to the flowchart illustrated
in Figure 5.7, which is based on the procedure presented in [31]. Similar to the P&O process, the
execution of the algorithm shown in Figure 5.7 is iteratively repeated until the difference between
and − is less than a predefined value, which indicates that the MPP has been tracked with
∂I pv I pv
∂V pv V pv
an acceptable accuracy.
Alternatively, the InC method may be implemented by controlling the power converter according
∂ I pv
to the sign of I pv + V pv such that its value is adjusted to zero as dictated by (5.6).
∂ V pv
Start the kth iteration
Measure I (k), V (k)
pv
pv
Calculate the deviations
(k)= V (k)–V (k–1)
V pv pv pv
I (k)= I (k)–I (k–1)
pv
pv
pv
I (k)/ V (k)> –I (k)/V (k)?
pv
pv
pv
pv
Yes No
ref
V ref (k)= V (k–1)+α V ref (k)=V (k–1)–α
ref
FIGURE 5.7 A flowchart of the InC MPPT algorithm based on the procedure presented in Elgendy et al.
(2013).