Page 356 - Reservoir Formation Damage
P. 356
336 Reservoir Formation Damage
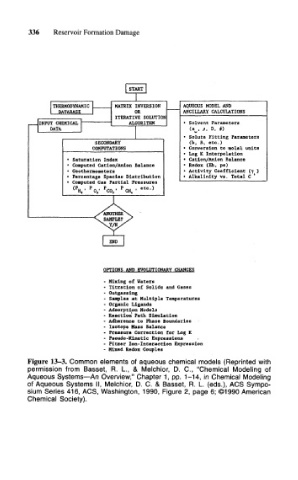
THERMODYNAMIC MATRIX INVERSION AQUEOUS MODEL AND
DATABASE OR ANCILLARY CALCULATIONS
ITERATIVE SOLUTIOt1
INPUT CHEMICAL ALGORITHM • Solvent Parameters
DATA (a^. p, D, ^)
• Solute Fitting Parameters
SECONDARY (b, B, etc.)
COMPUTATIONS Conversion to molal units
Log K Interpolation
• Saturation Index Cation/Anion Balance
• Computed Cation/Anlon Balance Redox (Eh, pe)
• Geotherraometers Activity Coefficient (7 )
• Percentage Species Distribution Alkalinity vs. Total C *
• Computed Gas Partial Pressures
( P P etC
V V CO,' CH. ' ->
OPTIONS AND EVOLUTIONARY CHANGES
- Mixing of Waters
- Titration of Solids and Gases
- Outgassing
- Samples at Multiple Temperatures
- Organic Ligands
- Adsorption Models
- Reaction Path Simulation
- Adherence to Phase Boundaries
- Isotope Mass Balance
- Pressure Correction for Log K
- Pseudo-Kinetic Expressions
- Pitzer Ion-Interaction Expression
- Mixed Redox Couples
Figure 13-3. Common elements of aqueous chemical models (Reprinted with
permission from Basset, R. L, & Melchior, D. C., "Chemical Modeling of
Aqueous Systems—An Overview," Chapter 1, pp. 1-14, in Chemical Modeling
of Aqueous Systems II, Melchior, D. C. & Basset, R. L. (eds.), ACS Sympo-
sium Series 416, ACS, Washington, 1990, Figure 2, page 6; ©1990 American
Chemical Society).