Page 359 - Robot Builder's Bonanza
P. 359
328 BUILD ROBOTS WITH LEGS
Build a 3- Servo Hexapod
Using simple linkages, you can construct a fully functional hexapod walking robot powered by
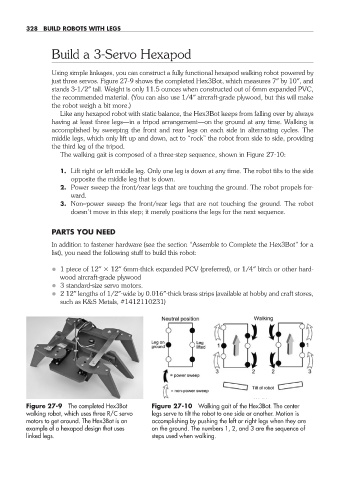
just three servos. Figure 27- 9 shows the completed Hex3Bot, which measures 7″ by 10″, and
stands 3- 1/2″ tall. Weight is only 11.5 ounces when constructed out of 6mm expanded PVC,
the recommended material. (You can also use 1/4″ aircraft- grade plywood, but this will make
the robot weigh a bit more.)
Like any hexapod robot with static balance, the Hex3Bot keeps from falling over by always
having at least three legs— in a tripod arrangement— on the ground at any time. Walking is
accomplished by sweeping the front and rear legs on each side in alternating cycles. The
middle legs, which only lift up and down, act to “rock” the robot from side to side, providing
the third leg of the tripod.
The walking gait is composed of a three- step sequence, shown in Figure 27- 10:
1. Lift right or left middle leg. Only one leg is down at any time. The robot tilts to the side
opposite the middle leg that is down.
2. Power sweep the front/rear legs that are touching the ground. The robot propels for-
ward.
3. Non–power sweep the front/rear legs that are not touching the ground. The robot
doesn’t move in this step; it merely positions the legs for the next sequence.
PARTS YOU NEED
In addition to fastener hardware (see the section “Assemble to Complete the Hex3Bot” for a
list), you need the following stuff to build this robot:
• 1 piece of 12″ 12″ 6mm- thick expanded PCV (preferred), or 1/4″ birch or other hard-
wood aircraft- grade plywood
• 3 standard- size servo motors.
• 2 12″ lengths of 1/2″-wide by 0.016″-thick brass strips (available at hobby and craft stores,
such as K&S Metals, #1412110231)
Figure 27- 9 The completed Hex3Bot Figure 27- 10 Walking gait of the Hex3Bot. The center
walking robot, which uses three R/C servo legs serve to tilt the robot to one side or another. Motion is
motors to get around. The Hex3Bot is an accomplishing by pushing the left or right legs when they are
example of a hexapod design that uses on the ground. The numbers 1, 2, and 3 are the sequence of
linked legs. steps used when walking.
27-chapter-27.indd 328 4/21/11 11:52 AM