Page 123 - Robot Builders Source Book - Gordon McComb
P. 123
112 Dynamic Analysis of Drives
m
Q° 7 i Q
TiO — .
n n ^o_-^^
j r i
—
m
2
FIGURE 3E-4a)
the time needed to achieve a speed of the piston V= 2m/sec when the height of the
mass increases; find the distance travelled by the piston. At the beginning of the process
the piston is at rest.
Exercise 3E-5
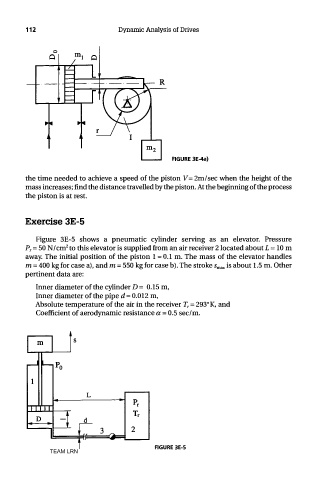
Figure 3E-5 shows a pneumatic cylinder serving as an elevator. Pressure
2
P r = 50 N/cm to this elevator is supplied from an air receiver 2 located about L = 10 m
away. The initial position of the piston 1 = 0.1 m. The mass of the elevator handles
m = 400 kg for case a), and m = 550 kg for case b). The stroke s max is about 1.5 m. Other
pertinent data are:
Inner diameter of the cylinder D = 0.15 m,
Inner diameter of the pipe d = 0.012 m,
Absolute temperature of the air in the receiver T r = 293° K, and
Coefficient of aerodynamic resistance a = 0.5 sec/m.
TEAM LRN FIGURE 3E-5