Page 103 - Robots Androids and Animatrons : 12 Incredible Projects You Can Build
P. 103
inform a robot if it is on an incline or decline, flat on its back or on
its stomach, or upside down or right side up. The robot can then
take appropriate action based on its body sense to accurately
change position.
Direction—magnetic fields
Using the Earth’s magnetic field, an electronic compass can provide
directional information. This will allow a robot to travel in a cer-
tain direction or to know which direction it’s traveling in.
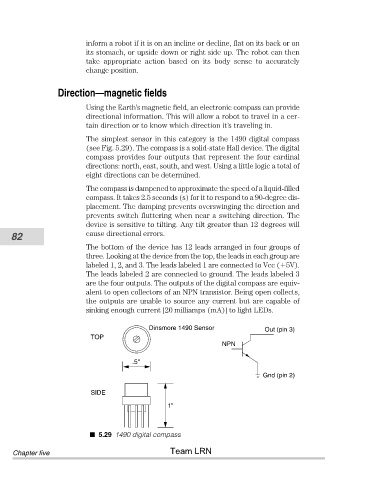
The simplest sensor in this category is the 1490 digital compass
(see Fig. 5.29). The compass is a solid-state Hall device. The digital
compass provides four outputs that represent the four cardinal
directions: north, east, south, and west. Using a little logic a total of
eight directions can be determined.
The compass is dampened to approximate the speed of a liquid-filled
compass. It takes 2.5 seconds (s) for it to respond to a 90-degree dis-
placement. The damping prevents overswinging the direction and
prevents switch fluttering when near a switching direction. The
device is sensitive to tilting. Any tilt greater than 12 degrees will
82 cause directional errors.
The bottom of the device has 12 leads arranged in four groups of
three. Looking at the device from the top, the leads in each group are
labeled 1, 2, and 3. The leads labeled 1 are connected to Vcc ( 5V).
The leads labeled 2 are connected to ground. The leads labeled 3
are the four outputs. The outputs of the digital compass are equiv-
alent to open collectors of an NPN transistor. Being open collects,
the outputs are unable to source any current but are capable of
sinking enough current [20 milliamps (mA)] to light LEDs.
Dinsmore 1490 Sensor Out (pin 3)
TOP
NPN
.5"
Gnd (pin 2)
SIDE
1"
5.29 1490 digital compass
Team LRN
Chapter five