Page 106 - Robots Androids and Animatrons : 12 Incredible Projects You Can Build
P. 106
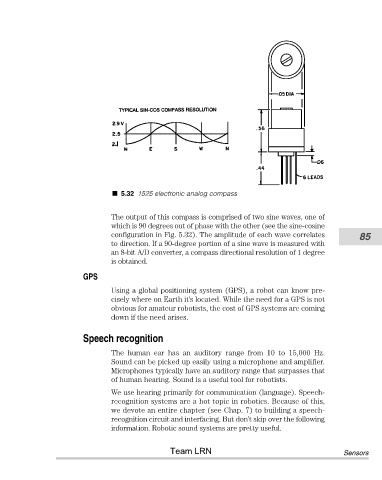
5.32 1525 electronic analog compass
The output of this compass is comprised of two sine waves, one of
which is 90 degrees out of phase with the other (see the sine-cosine
configuration in Fig. 5.32). The amplitude of each wave correlates 85
to direction. If a 90-degree portion of a sine wave is measured with
an 8-bit A/D converter, a compass directional resolution of 1 degree
is obtained.
GPS
Using a global positioning system (GPS), a robot can know pre-
cisely where on Earth it’s located. While the need for a GPS is not
obvious for amateur robotists, the cost of GPS systems are coming
down if the need arises.
Speech recognition
The human ear has an auditory range from 10 to 15,000 Hz.
Sound can be picked up easily using a microphone and amplifier.
Microphones typically have an auditory range that surpasses that
of human hearing. Sound is a useful tool for robotists.
We use hearing primarily for communication (language). Speech-
recognition systems are a hot topic in robotics. Because of this,
we devote an entire chapter (see Chap. 7) to building a speech-
recognition circuit and interfacing. But don’t skip over the following
information. Robotic sound systems are pretty useful.
Team LRN Sensors