Page 257 - Robots Androids and Animatrons : 12 Incredible Projects You Can Build
P. 257
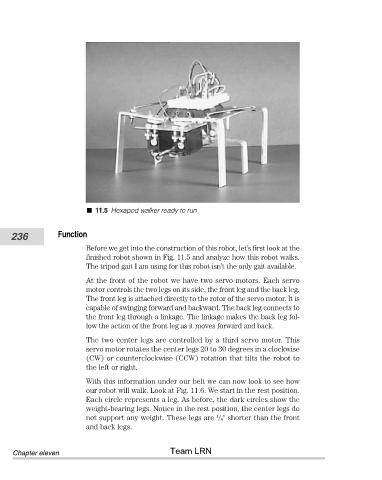
11.5 Hexapod walker ready to run
236 Function
Before we get into the construction of this robot, let’s first look at the
finished robot shown in Fig. 11.5 and analyze how this robot walks.
The tripod gait I am using for this robot isn’t the only gait available.
At the front of the robot we have two servo motors. Each servo
motor controls the two legs on its side, the front leg and the back leg.
The front leg is attached directly to the rotor of the servo motor. It is
capable of swinging forward and backward. The back leg connects to
the front leg through a linkage. The linkage makes the back leg fol-
low the action of the front leg as it moves forward and back.
The two center legs are controlled by a third servo motor. This
servo motor rotates the center legs 20 to 30 degrees in a clockwise
(CW) or counterclockwise (CCW) rotation that tilts the robot to
the left or right.
With this information under our belt we can now look to see how
our robot will walk. Look at Fig. 11.6. We start in the rest position.
Each circle represents a leg. As before, the dark circles show the
weight-bearing legs. Notice in the rest position, the center legs do
1
not support any weight. These legs are / 8" shorter than the front
and back legs.
Team LRN
Chapter eleven