Page 16 - Root Cause Failure Analysis
P. 16
General Analysis Techniques 7
+q I;
i
Acceptfailureeffed
disciplines
L..
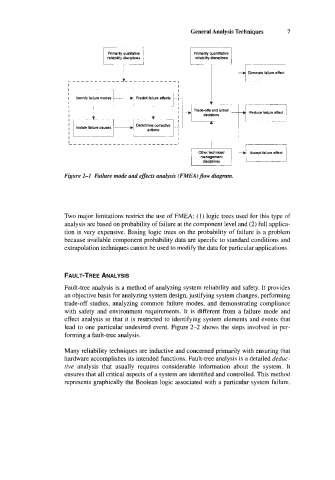
Figure 2-1 Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) flow diagram.
Two major limitations restrict the use of FMEA: (1) logic trees used for this type of
analysis are based on probability of failure at the component level and (2) full applica-
tion is very expensive. Basing logic trees on the probability of failure is a problem
because available component probability data are specific to standard conditions and
extrapolation techniques cannot be used to modify the data for particular applications.
FAULT-TREE ANALYSIS
Fault-tree analysis is a method of analyzing system reliability and safety. It provides
an objective basis for analyzing system design, justifying system changes, performing
trade-off studies, analyzing common failure modes, and demonstrating compliance
with safety and environment requirements. It is different from a failure mode and
effect analysis in that it is restricted to identifying system elements and events that
lead to one particular undesired event. Figure 2-2 shows the steps involved in per-
forming a fault-tree analysis.
Many reliability techniques are inductive and concerned primarily with ensuring that
hardware accomplishes its intended functions. Fault-tree analysis is a detailed deduc-
rive analysis that usually requires considerable information about the system. It
ensures that all critical aspects of a system are identified and controlled. This method
represents graphically the Boolean logic associated with a particular system failure.