Page 181 - Satellite Communications, Fourth Edition
P. 181
Antennas 161
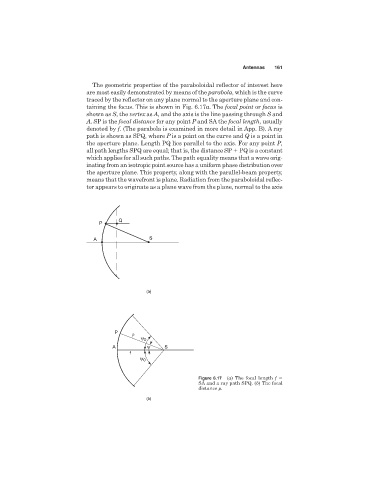
The geometric properties of the paraboloidal reflector of interest here
are most easily demonstrated by means of the parabola, which is the curve
traced by the reflector on any plane normal to the aperture plane and con-
taining the focus. This is shown in Fig. 6.17a.The focal point or focus is
shown as S,the vertex as A, and the axis is the line passing through S and
A. SP is the focal distance for any point P and SA the focal length, usually
denoted by f. (The parabola is examined in more detail in App. B). A ray
path is shown as SPQ, where P is a point on the curve and Q is a point in
the aperture plane. Length PQ lies parallel to the axis. For any point P,
all path lengths SPQ are equal; that is, the distance SP PQ is a constant
which applies for all such paths. The path equality means that a wave orig-
inating from an isotropic point source has a uniform phase distribution over
the aperture plane. This property, along with the parallel-beam property,
means that the wavefront is plane. Radiation from the paraboloidal reflec-
tor appears to originate as a plane wave from the plane, normal to the axis
Q
P
A S
(a)
P ρ
ψ 0
A ψ S
f
ψ 0
Figure 6.17 (a) The focal length f
SA and a ray path SPQ. (b) The focal
distance .
(b)