Page 215 - Schaum's Outline of Differential Equations
P. 215
198 SOLVING SECOND-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS [CHAP. 20
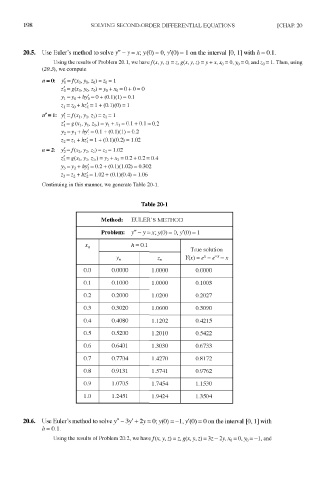
20.5. Use Euler's method to solve /' - y = x; y (0) = 0, /(O) = 1 on the interval [0,1] with h = 0.1.
Using the results of Problem 20.1, we have/(jt, y, z) = z, g(x, y,z)=y + x,x 0 = 0, y 0 = 0, and z 0 = 1. Then, using
(20.3), we compute
Continuing in this manner, we generate Table 20-1.
Table 20-1
Method: EULER'S METHOD
Problem: y" - y = x; y(0) = 0, /(O) = 1
ft = 0.1
x n
True solution
y n Zn Y(x) = e -e~ -x
x
x
0.0 0.0000 1.0000 0.0000
0.1 0.1000 1.0000 0.1003
0.2 0.2000 1.0200 0.2027
0.3 0.3020 1.0600 0.3090
0.4 0.4080 1.1202 0.4215
0.5 0.5200 1.2010 0.5422
0.6 0.6401 1.3030 0.6733
0.7 0.7704 1.4270 0.8172
0.8 0.9131 1.5741 0.9762
0.9 1.0705 1.7454 1.1530
1.0 1.2451 1.9424 1.3504
20.6. Use Euler's method to solve y" - 3y' + 2y = 0; y(0) = -1, /(O) = 0 on the interval [0, 1] with
A = 0.1.
Using the results of Problem 20.2, we have/(jc, y, z) = Z, g(x, y, z) = 3z — 2y, x 0 = 0,y 0 = —1, and