Page 220 - Schaum's Outline of Differential Equations
P. 220
CHAP. 20] SOLVING SECOND-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 203
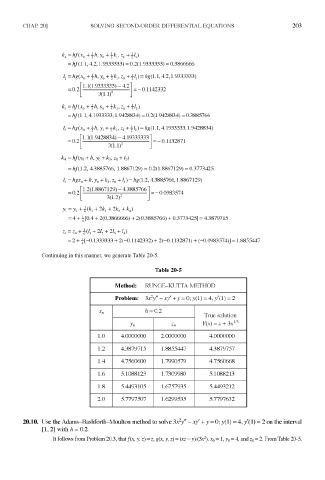
Continuing in this manner, we generate Table 20-5.
Table 20-5
Method: RUNGE-KUTTA METHOD
2
Problem: 3x y" -xy' + y = 0; y(l) = 4, /(I) = 2
ft = 0.2
x n
True solution
y n •^n Y(x) = x + 3x 113
•7
1.0 4.0000000 2.0000000 4.0000000
1.2 4.3879715 1.8855447 4.3879757
1.4 4.7560600 1.7990579 4.7560668
1.6 5.1088123 1.7309980 5.1088213
1.8 5.4493105 1.6757935 5.4493212
2.0 5.7797507 1.6299535 5.7797632
2
20.10. Use the Adams-Bashforth-Moulton method to solve 3.x )/' - xy' + y = 0; y(l) = 4, /(I) = 2 on the interval
[1,2] with/; = 0.2.
It follows from Problem 20.3, that/(^, y, z) = z, g(x, y, z) = (xz - y)/^), X 0=l,y 0 = 4,andz 0 = 2. From Table 20-5,