Page 100 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Electric Circuits
P. 100
AMPLIFIERS AND OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS
CHAP. 5]
Fig. 5-36 89
ðv v 1 Þg 1 þðv v 2 Þg 2 þðv v 3 Þg 3 ¼ 0
v 1 g 1 þ v 2 g 2 þ v 3 g 3 v 1 R 2 R 3 þ v 2 R 1 R 3 þ v 3 R 2 R 1
Then v ¼ ¼
g 1 þ g 2 þ g 3 R 1 R 2 þ R 2 R 3 þ R 3 R 1
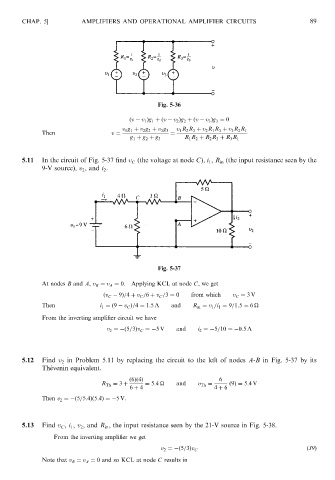
5.11 In the circuit of Fig. 5-37 find v C (the voltage at node C), i 1 , R in (the input resistance seen by the
9-V source), v 2 ,and i 2 .
Fig. 5-37
At nodes B and A, v B ¼ v A ¼ 0. Applying KCL at node C, we get
ðv C 9Þ=4 þ v C =6 þ v C =3 ¼ 0 from which v C ¼ 3V
Then i 1 ¼ð9 v C Þ=4 ¼ 1:5 A and R in ¼ v 1 =i 1 ¼ 9=1:5 ¼ 6
From the inverting amplifier circuit we have
v 2 ¼ ð5=3Þv C ¼ 5 V and i 2 ¼ 5=10 ¼ 0:5A
5.12 Find v 2 in Problem 5.11 by replacing the circuit to the left of nodes A-B in Fig. 5-37 by its
The ´ venin equivalent.
ð6Þð4Þ 6
R Th ¼ 3 þ ¼ 5:4
and v Th ¼ ð9Þ¼ 5:4V
6 þ 4 4 þ 6
Then v 2 ¼ ð5=5:4Þð5:4Þ¼ 5V.
5.13 Find v C , i 1 , v 2 ,and R in , the input resistance seen by the 21-V source in Fig. 5-38.
From the inverting amplifier we get
v 2 ¼ ð5=3Þv C ð39Þ
Note that v B ¼ v A ¼ 0 and so KCL at node C results in