Page 171 - Science at the nanoscale
P. 171
RPS: PSP0007 - Science-at-Nanoscale
10:16
June 5, 2009
are designed to work in the visible light regime (400–700nm), the
smallest features that are resolvable are about the size of half the
wavelength of light used (approx. 200 nm). In order words, any
two features that are closer than half the wavelength of the light
would be regarded as a single feature. Thus optical microscopes
have limited resolution in the nanoscale regime.
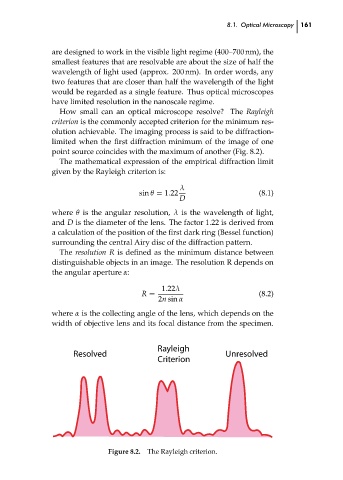
How small can an optical microscope resolve? The Rayleigh
criterion is the commonly accepted criterion for the minimum res-
olution achievable. The imaging process is said to be diffraction-
limited when the first diffraction minimum of the image of one
point source coincides with the maximum of another (Fig. 8.2).
The mathematical expression of the empirical diffraction limit
given by the Rayleigh criterion is:
λ
(8.1)
sin θ = 1.22
D
where θ is the angular resolution, λ is the wavelength of light,
and D is the diameter of the lens. The factor 1.22 is derived from
a calculation of the position of the first dark ring (Bessel function)
surrounding the central Airy disc of the diffraction pattern.
The resolution R is defined as the minimum distance between
distinguishable objects in an image. The resolution R depends on
the angular aperture α:
1.22λ
(8.2)
R =
2n sin α
where α is the collecting angle of the lens, which depends on the
width of objective lens and its focal distance from the specimen.
Rayleigh 8.1. Optical Microscopy 161 ch08
Resolved Unresolved
Criterion
Figure 8.2. The Rayleigh criterion.