Page 252 - Sedimentology and Stratigraphy
P. 252
Types of Carbonate Platform 239
hummocky and swaley cross-stratification (14.2.1). In
deeper water below storm wave base the outer ramp
deposits are principally redeposited carbonate mud-
stone and wackestone, often with the characteristics
of turbidites. Redeposition of carbonate sediments is
common in situations where the outer edge of the
ramp merges into a steeper slope at a continental
margin as a distally steepened ramp. Homoclinal
ramps have a consistent gentle slope on which little
reworking of material by mass-flow processes occurs
(Read 1985). In contrast to rimmed shelves reefal
build-ups are relatively rare in ramp settings. Isolated
patch reefs may occur in the more proximal parts of a
ramp and mud mounds are known from Palaeozoic
ramp environments.
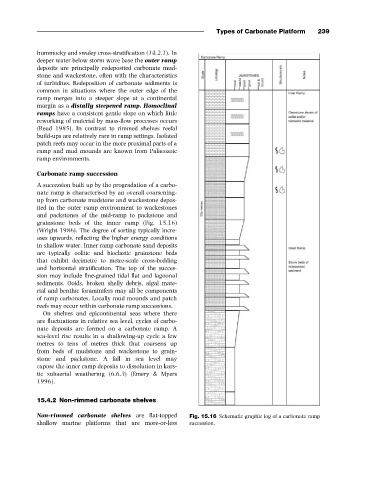
Carbonate ramp succession
A succession built up by the progradation of a carbo-
nate ramp is characterised by an overall coarsening-
up from carbonate mudstone and wackestone depos-
ited in the outer ramp environment to wackestones
and packstones of the mid-ramp to packstone and
grainstone beds of the inner ramp (Fig. 15.16)
(Wright 1986). The degree of sorting typically incre-
ases upwards, reflecting the higher energy conditions
in shallow water. Inner ramp carbonate sand deposits
are typically oolitic and bioclastic grainstone beds
that exhibit decimetre to metre-scale cross-bedding
and horizontal stratification. The top of the succes-
sion may include fine-grained tidal flat and lagoonal
sediments. Ooids, broken shelly debris, algal mate-
rial and benthic foraminifers may all be components
of ramp carbonates. Locally mud mounds and patch
reefs may occur within carbonate ramp successions.
On shelves and epicontinental seas where there
are fluctuations in relative sea level, cycles of carbo-
nate deposits are formed on a carbonate ramp. A
sea-level rise results in a shallowing-up cycle a few
metres to tens of metres thick that coarsens up
from beds of mudstone and wackestone to grain-
stone and packstone. A fall in sea level may
expose the inner ramp deposits to dissolution in kars-
tic subaerial weathering (6.6.3) (Emery & Myers
1996).
15.4.2 Non-rimmed carbonate shelves
Non-rimmed carbonate shelves are flat-topped Fig. 15.16 Schematic graphic log of a carbonate ramp
shallow marine platforms that are more-or-less succession.