Page 214 - Separation process principles 2
P. 214
5.7 Degrees of Freedom and Specifications for Countercurrent Cascades 179
Specification of these (2C + 6) variables permits calcu- adiabatic or nonadiabatic equilibrium-stage element, the
lation of the unknown variables LOUT, VOUT, (x~)~,~, total number of variables from (5-68) is
(ye) vrN, all (x, )LOUT, TOUT, and all (yi) v0,, , where C denotes
the missing mole fractions in the two entering streams. (Nvlunit = N(4C + 13) - [2(N - l)](C + 3) + 1
=7N+2NC+2C+7
single-Section, Countercurrent Cascade since 2(N - 1) interconnecting streams exist. The addi-
tional variable is the total number of stages (i.e., NA = 1).
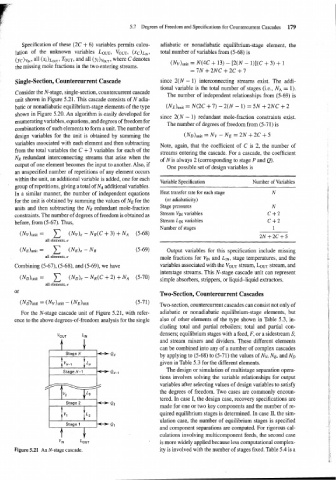
Consider the N-stage, single-section, countercurrent cascade
The number of independent relationships from (5-69) is
unit shown in Figure 5.21. This cascade consists of N adia-
batic or nonadiabatic equilibrium-stage elements of the type (N~)unlt = N(2C + 7) - 2(N - 1) = 5N + 2NC + 2
shown in Figure 5'20 An Is for since 2(N - 1) redundant mole-fraction constraints exist,
enumerating variables, equations, and degrees of freedom for
The number of degrees of freedom from (5-7 is
combinations of such elements to form a unit. The number of
design variables for the unit is obtained by summing the
variables associated with each element and then subtracting Note, again, that the coefficient of C is 2, the number of
from the total variables the C + 3 variables for each of the
streams entering the cascade. For a cascade, the coefficient
NR redundant interconnecting streams that arise when the
of N is always 2 (corresponding to stage P and Q).
output of one element becomes the input to another. Also, if One possible set of design variables is
an unspecified number of repetitions of any element occurs
within the unit, an additional variable is added, one for each
Variable Specification Number of Variables
group of repetitions, giving a total of NA additional variables.
In a similar manner, the number of independent equations Heat transfer rate for each stage N
for the unit is obtained by summing the values of NE for the (or adiabaticity)
units and then subtracting the NR redundant mole-fraction Stage pressures N
constraints. The number of degrees of freedom is obtained as Stream VN variables C+2
before, from (5-67). Thus, Stream LN variables C+2
Number of stages 1
2N+2C+5
all elements, e
(N~Iunit = 1 (NEL - NR (5-69) Output variables for this specification include missing
all elements, e mole fractions for Vm and LIN, stage temperatures, and the
Combining (5-67), (5-68), and (5-69), we have variables associated with the VoUT stream, LOUT stream, and
interstage streams. This N-stage cascade unit can represent
(N~)unit = C (ND)~ - NR(C + 2) + NA (5-70) simple absorbers, strippers, or liquid-liquid extractors.
all elements, e
or
Two-Section, Countercurrent Cascades
Two-section, countercurrent cascades can consist not only of
For the N-stage cascade unit of Figure 5.21, with refer- adiabatic or nonadiabatic equilibrium-stage elements, but
ence to the above degrees-of-freedom analysis for the single also of other elements of the type shown in Table 5.3, in-
cluding total and partial reboilers; total and partial con-
densers; equilibriuh stages with a feed, F, or a sidestream S;
and stream mixers and dividers. These different elements
can be combined into any of a number of complex cascades
Ei- by applying to (5-68) to (5-71) the values of Nv, NE, and ND
Stage N
given in Table 5.3 for the different elements.
w tions involves solving the variable relationships for output
The design or simulation of multistage separation opera-
Stage N-I
QN-i
Q~
variables after selecting values of design variables to satisfy
the degrees of freedom. Two cases are commonly encoun-
tered. In case I, the design case, recovery specifications are
Stage 2
made for one or two key components and the number of re-
quired equilibrium stages is determined. In case 11, the sim-
ulation case, the number of equilibrium stages is specified
Q2
Stage 1
ITWQ1 and component separations are computed. For rigorous cal-
culations involving multicomponent feeds, the second case
VI N L~~~ is more widely applied because less computational complex-
Figure 5.21 An N-stage cascade. ity is involved with the number of stages fixed. Table 5.4 is a