Page 211 - Separation process principles 2
P. 211
176 Chapter 5 Cascades and Hybrid Systems
vapor. Not shown in Figure 5.17 are recycle gas compres-
sors. Typical calculations of Prasad et al. [6] give the fol-
lowing results: 1
Permeate
Membrane Mol% N2 % Recovery (a) Membrane alone
System in Retentate of N2 Adsorbate
CH,-rich
Single stage 98 45
Two-stage cascade 99.5 48
I I
Three-stage cascade 99.9 50 Exhaust
These results show that a high purity can be obtained with (b) Adsorption alone
a single-section membrane cascade, but without major im-
provement in the recovery. To obtain both high purity and
high recovery, a two-section membrane cascade is neces- r
sary, as discussed in Section 14.3. Recycle
5.6 HYBRID SYSTEMS
I N,-rich
To reduce costs, particularly energy cost, make possible a I t
difficult separation, andlor improve the degree of separation, (c) Adsorption-membrane hybrid
hybrid systems, consisting of two or more separation opera-
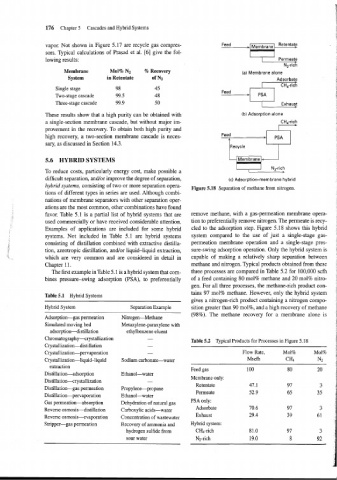
Figure 5.18 Separation of methane from nitrogen.
tions of different types in series are used. Although combi-
nations of membrane separators with other separation oper-
ations are the most common, other combinations have found
favor. Table 5.1 is a partial list of hybrid systems that are remove methane, with a gas-permeation membrane opera-
used commercially or have received considerable attention. tion to preferentially remove nitrogen. The permeate is recy-
Examples of applications are included for some hybrid cled to the adsorption step. Figure 5.18 shows this hybrid
systems. Not included in Table 5.1 are hybrid systems system compared to the use of just a single-stage gas-
consisting of distillation combined with extractive distilla- permeation membrane operation and a single-stage pres-
tion, azeotropic distillation, andlor liquid-liquid extraction, sure-swing adsorption operation. Only the hybrid system is
which are very common and are considered in detail in capable of making a relatively sharp separation between
Chapter 11. methane and nitrogen. Typical products obtained from these
The first example in Table 5.1 is a hybrid system that com- three processes are compared in Table 5.2 for 100,000 scfh
bines pressure-swing adsorption (PSA), to preferentially of a feed containing 80 mol% methane and 20 mol% nitro-
gen. For all three processes, the methane-rich product con-
tains 97 mol% methane. However, only the hybrid system
Table 5.1 Hybrid Systems
gives a nitrogen-rich product containing a nitrogen compo-
Hybrid System Separation Example sition greater than 90 mol%, and a high recovery of methane
(98%). The methane recovery for a membrane alone is
Adsorption-gas permeation Nitrogen-Methane
Simulated moving bed Metaxylene-parax ylene with
adsorption-distillation ethylbenzene eluent
Chromatography-crystallization -
Table 5.2 Typical Products for Processes in Figure 5.18
Crystallization-distillation -
Crystallization-pervaporation - Flow Rate, Mol% Mol%
Crystallization-liquid-liquid Sodium carbonate-water Mscfh CH4 Nz
extraction
Feed gas 100 80 20
Distillation-adsorption Ethanol-water
Membrane only:
Distillation-crystallization -
Retentate 47.1 97 3
Distillation-gas permeation Propy lene-propane
Permeate 52.9 65 35
Distillalion-pervaporation Ethanol-water
PSA only:
Gas permeation-absorption Dehydration of natural gas
Reverse osmosis4istillation Carboxylic acids-water Adsorbate 70.6 97 3
Reverse osmosis-evaporation Concentration of wastewater Exhaust 29.4 39 61
Stripper-gas permeation Recovery of ammonia and Hybrid system:
hydrogen sulfide from CH4-rich 81.0 97 3
sour water Nz-rich 19.0 8 92