Page 86 - Separation process principles 2
P. 86
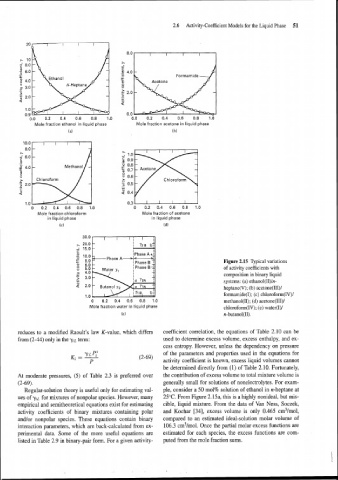
2.6 Activity-Coefficient Models for the Liquid Phase 51
Mole fraction ethanol in liquid phase Mole fraction acetone in liquid phase
(a) (b)
I I I I
-
-
Chloroform
1 .o 0.3
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
Mole fraction chloroform Mole fraction of acetone
in liquid phase in liquid phase
(c) (d)
-
I 72 B b-:
-
I I
- ;Phase At1
Phase A- +I
- Figure 2.15 Typical variations
of activity coefficients with
composition in binary liquid
systems: (a) ethanol(I1)ln-
heptane(V); (b) acetone(I1I)l
formamide(1); (c) chloroform(IV)/
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 methanol(I1); (d) acetone(III)/
Mole fraction water in liquid phase chloroform(1V); (e) water(I)/
(e) n-butanol(I1).
reduces to a modified Raoult's law K-value, which differs coefficient correlation, the equations of Table 2.10 can be
from (2-44) only in the -yi~ term: used to determine excess volume, excess enthalpy, and ex-
cess entropy. However, unless the dependency on pressure
of the parameters and properties used in the equations for
activity coefficient is known, excess liquid volumes cannot
be determined directly from (1) of Table 2.10. Fortunately,
At moderate pressures, (5) of Table 2.3 is preferred over the contribution of excess volume to total mixture volume is
(2-69). generally small for solutions of nonelectrolytes. For exam-
Regular-solution theory is useful only for estimating val- ple, consider a 50 mol% solution of ethanol in n-heptane at
ues of -y,~ for mixtures of nonpolar species. However, many 25°C. From Figure 2.15a, this is a highly nonideal, but rnis-
empirical and semitheoretical equations exist for estimating cible, liquid mixture. From the data of Van Ness, Soczek,
activity coefficients of binary mixtures containing polar and Kochar [34], excess volume is only 0.465 cm3/mol,
andlor nonpolar species. These equations contain binary compared to an estimated ideal-solution molar volume of
interaction parameters, which are back-calculated from ex- 106.3 cm3/mol. Once the partial molar excess functions are
perimental data. Some of the more useful equations are estimated for each species, the excess functions are com-
listed in Table 2.9 in binary-pair form. For a given activity- puted from the mole fraction sums.