Page 211 - Serious Incident Prevention How to Achieve and Sustain Accident-Free Operations in Your Plant or Company
P. 211
CH15pp159-189 4/10/02 12:51 PM Page 177
Applying the Process Model—A Case Study 177
TABLE 15-5 continued
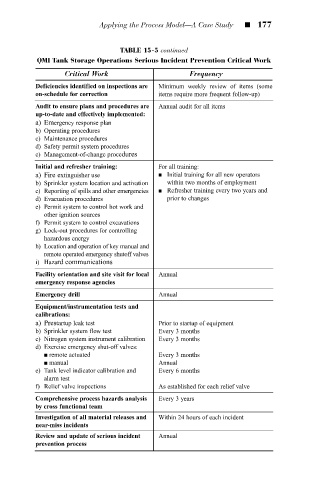
QMI Tank Storage Operations Serious Incident Prevention Critical Work
Critical Work Frequency
Deficiencies identified on inspections are Minimum weekly review of items (some
on-schedule for correction items require more frequent follow-up)
Audit to ensure plans and procedures are Annual audit for all items
up-to-date and effectively implemented:
a) Emergency response plan
b) Operating procedures
c) Maintenance procedures
d) Safety permit system procedures
e) Management-of-change procedures
Initial and refresher training: For all training:
a) Fire extinguisher use Initial training for all new operators
b) Sprinkler system location and activation within two months of employment
c) Reporting of spills and other emergencies Refresher training every two years and
d) Evacuation procedures prior to changes
e) Permit system to control hot work and
other ignition sources
f) Permit system to control excavations
g) Lock-out procedures for controlling
hazardous energy
h) Location and operation of key manual and
remote operated emergency shutoff valves
i) Hazard communications
Facility orientation and site visit for local Annual
emergency response agencies
Emergency drill Annual
Equipment/instrumentation tests and
calibrations:
a) Prestartup leak test Prior to startup of equipment
b) Sprinkler system flow test Every 3 months
c) Nitrogen system instrument calibration Every 3 months
d) Exercise emergency shut-off valves:
remote actuated Every 3 months
manual Annual
e) Tank level indicator calibration and Every 6 months
alarm test
f) Relief valve inspections As established for each relief valve
Comprehensive process hazards analysis Every 3 years
by cross functional team
Investigation of all material releases and Within 24 hours of each incident
near-miss incidents
Review and update of serious incident Annual
prevention process