Page 414 - Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design
P. 414
bud29281_ch07_358-408.qxd 12/8/09 12:52PM Page 389 ntt 203:MHDQ196:bud29281:0073529281:bud29281_pagefiles:
Shafts and Shaft Components 389
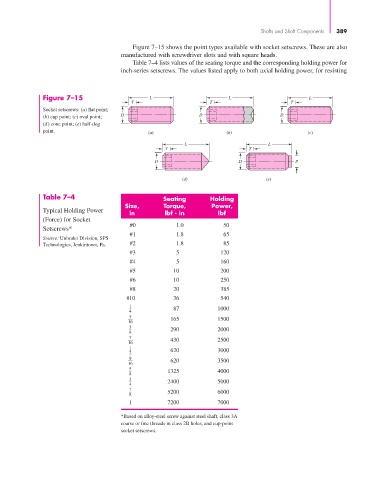
Figure 7–15 shows the point types available with socket setscrews. These are also
manufactured with screwdriver slots and with square heads.
Table 7–4 lists values of the seating torque and the corresponding holding power for
inch-series setscrews. The values listed apply to both axial holding power, for resisting
Figure 7–15 L L L
T T T
Socket setscrews: (a) flat point;
D D D
(b) cup point; (c) oval point;
(d) cone point; (e) half-dog
point. (a) (b) (c)
L L
T T
D D P
(d) (e)
Table 7–4 Seating Holding
Size, Torque, Power,
Typical Holding Power
in lbf . in lbf
(Force) for Socket
#0 1.0 50
Setscrews*
#1 1.8 65
Source: Unbrako Division, SPS
Technologies, Jenkintown, Pa. #2 1.8 85
#3 5 120
#4 5 160
#5 10 200
#6 10 250
#8 20 385
#10 36 540
1 87 1000
4
5
16 165 1500
3 290 2000
8
7
16 430 2500
1 620 3000
2
9
16 620 3500
5 1325 4000
8
3 2400 5000
4
7 5200 6000
8
1 7200 7000
*Based on alloy-steel screw against steel shaft, class 3A
coarse or fine threads in class 2B holes, and cup-point
socket setscrews.