Page 449 - Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design
P. 449
bud29281_ch08_409-474.qxd 12/16/2009 7:11 pm Page 424 pinnacle 203:MHDQ196:bud29281:0073529281:bud29281_pagefiles:
424 Mechanical Engineering Design
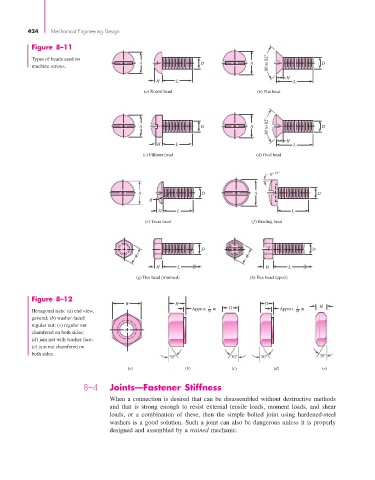
Figure 8–11
Types of heads used on
machine screws. A D A 80 to 82° D
H
H L L
(a) Round head (b) Flat head
A D A 80 to 82° D
H
H L L
(c) Fillister head (d) Oval head
5° ±3°
A D A D
R
H L L
(e) Truss head (f) Binding head
D D
W W
H L H L
(g) Hex head (trimmed) (h) Hex head (upset)
Figure 8–12
W H H H
Hexagonal nuts: (a) end view, Approx. 64 1 in H Approx. 64 1 in
general; (b) washer-faced
regular nut; (c) regular nut
chamfered on both sides;
(d) jam nut with washer face;
(e) jam nut chamfered on
both sides.
30 30 30 30
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
8–4 Joints—Fastener Stiffness
When a connection is desired that can be disassembled without destructive methods
and that is strong enough to resist external tensile loads, moment loads, and shear
loads, or a combination of these, then the simple bolted joint using hardened-steel
washers is a good solution. Such a joint can also be dangerous unless it is properly
designed and assembled by a trained mechanic.