Page 458 - Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design
P. 458
bud29281_ch08_409-474.qxd 12/16/2009 7:11 pm Page 433 pinnacle 203:MHDQ196:bud29281:0073529281:bud29281_pagefiles:
Screws, Fasteners, and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints 433
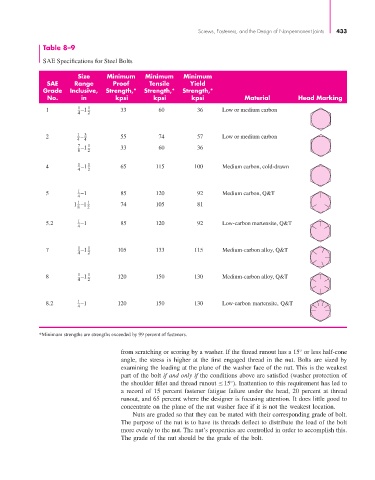
Table 8–9
SAE Specifications for Steel Bolts
Size Minimum Minimum Minimum
SAE Range Proof Tensile Yield
Grade Inclusive, Strength,* Strength,* Strength,*
No. in kpsi kpsi kpsi Material Head Marking
1 1 –1 1 33 60 36 Low or medium carbon
4 2
2 1 – 3 55 74 57 Low or medium carbon
4 4
7 –1 1 33 60 36
8 2
4 1 –1 1 65 115 100 Medium carbon, cold-drawn
4 2
5 1 –1 85 120 92 Medium carbon, Q&T
4
1
1 –1 1 74 105 81
8 2
5.2 1 –1 85 120 92 Low-carbon martensite, Q&T
4
7 1 –1 1 105 133 115 Medium-carbon alloy, Q&T
4 2
8 1 –1 1 120 150 130 Medium-carbon alloy, Q&T
4 2
8.2 1 –1 120 150 130 Low-carbon martensite, Q&T
4
*Minimum strengths are strengths exceeded by 99 percent of fasteners.
from scratching or scoring by a washer. If the thread runout has a 15 or less half-cone
◦
angle, the stress is higher at the first engaged thread in the nut. Bolts are sized by
examining the loading at the plane of the washer face of the nut. This is the weakest
part of the bolt if and only if the conditions above are satisfied (washer protection of
the shoulder fillet and thread runout ≤15 ). Inattention to this requirement has led to
◦
a record of 15 percent fastener fatigue failure under the head, 20 percent at thread
runout, and 65 percent where the designer is focusing attention. It does little good to
concentrate on the plane of the nut washer face if it is not the weakest location.
Nuts are graded so that they can be mated with their corresponding grade of bolt.
The purpose of the nut is to have its threads deflect to distribute the load of the bolt
more evenly to the nut. The nut’s properties are controlled in order to accomplish this.
The grade of the nut should be the grade of the bolt.