Page 455 - Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design
P. 455
bud29281_ch08_409-474.qxd 12/16/2009 7:11 pm Page 430 pinnacle 203:MHDQ196:bud29281:0073529281:bud29281_pagefiles:
430 Mechanical Engineering Design
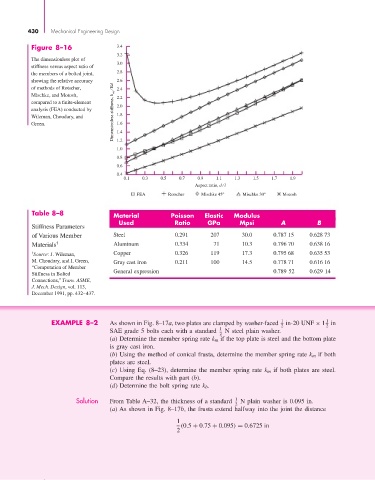
Figure 8–16 3.4
3.2
The dimensionless plot of
3.0
stiffness versus aspect ratio of
the members of a bolted joint, 2.8
showing the relative accuracy 2.6
of methods of Rotscher, ⁄ Ed 2.4
Mischke, and Motosh, 2.2
compared to a finite-element
analysis (FEA) conducted by 2.0
Wileman, Choudury, and Dimensionless stiffness, k m 1.8
Green. 1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.1 0.3 0.5 0.7 0.9 1.1 1.3 1.5 1.7 1.9
Aspect ratio, d ⁄ l
FEA Rotscher Mischke 45° Mischke 30° Motosh
Table 8–8 Material Poisson Elastic Modulus
Stiffness Parameters Used Ratio GPa Mpsi A B
of Various Member Steel 0.291 207 30.0 0.787 15 0.628 73
Materials † Aluminum 0.334 71 10.3 0.796 70 0.638 16
† Source: J. Wileman, Copper 0.326 119 17.3 0.795 68 0.635 53
M. Choudury, and I. Green, Gray cast iron 0.211 100 14.5 0.778 71 0.616 16
“Computation of Member
Stiffness in Bolted General expression 0.789 52 0.629 14
Connections,” Trans. ASME,
J. Mech. Design, vol. 113,
December 1991, pp. 432–437.
1
1
EXAMPLE 8–2 As shown in Fig. 8–17a, two plates are clamped by washer-faced in-20 UNF × 1 in
2
2
SAE grade 5 bolts each with a standard 1 2 N steel plain washer.
(a) Determine the member spring rate k m if the top plate is steel and the bottom plate
is gray cast iron.
(b) Using the method of conical frusta, determine the member spring rate k m if both
plates are steel.
(c) Using Eq. (8–23), determine the member spring rate k m if both plates are steel.
Compare the results with part (b).
(d) Determine the bolt spring rate k b .
Solution From Table A–32, the thickness of a standard 1 2 N plain washer is 0.095 in.
(a) As shown in Fig. 8–17b, the frusta extend halfway into the joint the distance
1 (0.5 + 0.75 + 0.095) = 0.6725 in
2