Page 491 - Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design
P. 491
bud29281_ch08_409-474.qxd 12/16/2009 7:11 pm Page 466 pinnacle 203:MHDQ196:bud29281:0073529281:bud29281_pagefiles:
466 Mechanical Engineering Design
A
Problem 8–46 B
C
d
(a) Find the wrench torque required if the fasteners are lubricated during assembly and the joint
is to be permanent.
(b) Determine the factors of safety guarding against yielding, overload, and joint separation.
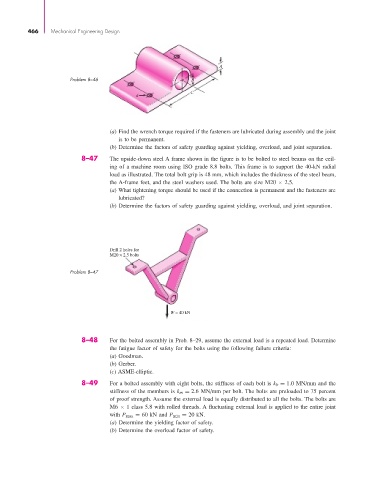
8–47 The upside-down steel A frame shown in the figure is to be bolted to steel beams on the ceil-
ing of a machine room using ISO grade 8.8 bolts. This frame is to support the 40-kN radial
load as illustrated. The total bolt grip is 48 mm, which includes the thickness of the steel beam,
the A-frame feet, and the steel washers used. The bolts are size M20 × 2.5.
(a) What tightening torque should be used if the connection is permanent and the fasteners are
lubricated?
(b) Determine the factors of safety guarding against yielding, overload, and joint separation.
Drill 2 holes for
M20 × 2.5 bolts
Problem 8–47
W = 40 kN
8–48 For the bolted assembly in Prob. 8–29, assume the external load is a repeated load. Determine
the fatigue factor of safety for the bolts using the following failure criteria:
(a) Goodman.
(b) Gerber.
(c) ASME-elliptic.
8–49 For a bolted assembly with eight bolts, the stiffness of each bolt is k b = 1.0 MN/mm and the
stiffness of the members is k m = 2.6 MN/mm per bolt. The bolts are preloaded to 75 percent
of proof strength. Assume the external load is equally distributed to all the bolts. The bolts are
M6 × 1 class 5.8 with rolled threads. A fluctuating external load is applied to the entire joint
with P max = 60 kN and P min = 20 kN.
(a) Determine the yielding factor of safety.
(b) Determine the overload factor of safety.