Page 419 -
P. 419
422 M. Neumann
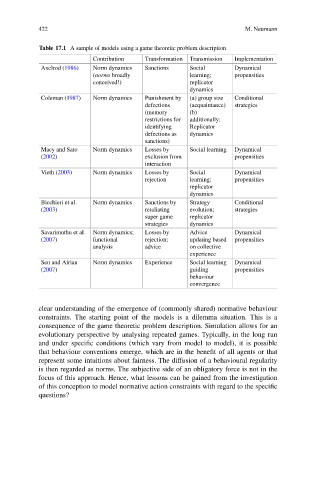
Table 17.1 A sample of models using a game theoretic problem description
Contribution Transformation Transmission Implementation
Axelrod (1986) Norm dynamics Sanctions Social Dynamical
(norms broadly learning; propensities
conceived!) replicator
dynamics
Coleman (1987) Norm dynamics Punishment by (a) group size Conditional
defections (acquaintance) strategies
(memory (b)
restrictions for additionally:
identifying Replicator
defections as dynamics
sanctions)
Macy and Sato Norm dynamics Losses by Social learning Dynamical
(2002) exclusion from propensities
interaction
Vieth (2003) Norm dynamics Losses by Social Dynamical
rejection learning; propensities
replicator
dynamics
Bicchieri et al. Norm dynamics Sanctions by Strategy Conditional
(2003) retaliating evolution; strategies
super game replicator
strategies dynamics
Savarimuthu et al. Norm dynamics; Losses by Advice Dynamical
(2007) functional rejection; updating based propensities
analysis advice on collective
experience
Sen and Airiau Norm dynamics Experience Social learning Dynamical
(2007) guiding propensities
behaviour
convergence
clear understanding of the emergence of (commonly shared) normative behaviour
constraints. The starting point of the models is a dilemma situation. This is a
consequence of the game theoretic problem description. Simulation allows for an
evolutionary perspective by analysing repeated games. Typically, in the long run
and under specific conditions (which vary from model to model), it is possible
that behaviour conventions emerge, which are in the benefit of all agents or that
represent some intuitions about fairness. The diffusion of a behavioural regularity
is then regarded as norms. The subjective side of an obligatory force is not in the
focus of this approach. Hence, what lessons can be gained from the investigation
of this conception to model normative action constraints with regard to the specific
questions?