Page 263 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 263
250 Soil and Water Contamination
6642 6642 6642
k max
0.5 k
0
C
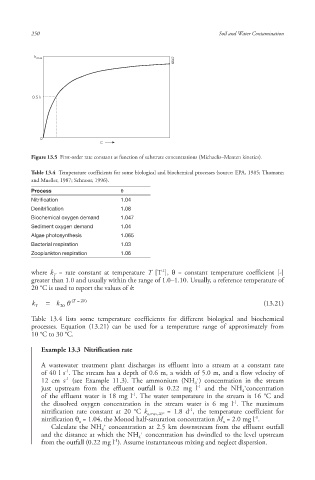
Figure 13.5 First-order rate constant as function of substrate concentrations (Michaelis–Menten kinetics ).
Table 13.4 Temperature coefficients for some biological and biochemical processes (source: EPA, 1985; Thomann
and Mueller, 1987; Schnoor, 1996).
Process θ
Nitrification 1.04
Denitrification 1.08
Biochemical oxygen demand 1.047
Sediment oxygen demand 1.04
Algae photosynthesis 1.065
Bacterial respiration 1.03
Zooplankton respiration 1.06
-1
where k = rate constant at temperature T [T ], θ = constant temperature coefficient [-]
T
greater than 1.0 and usually within the range of 1.0–1.10. Usually, a reference temperature of
20 °C is used to report the values of k:
k k (T 20 ) (13.21)
T 20
Table 13.4 lists some temperature coefficients for different biological and biochemical
processes. Equation (13.21) can be used for a temperature range of approximately from
10 °C to 30 °C.
Example 13.3 Nitrification rate
A wastewater treatment plant discharges its effluent into a stream at a constant rate
-1
of 40 l s . The stream has a depth of 0.6 m, a width of 5.0 m, and a flow velocity of
+
-1
12 cm s (see Example 11.3). The ammonium (NH ) concentration in the stream
4
-1
+
just upstream from the effluent outfall is 0.22 mg l and the NH concentration
4
-1
of the effluent water is 18 mg l . The water temperature in the stream is 16 °C and
-1
the dissolved oxygen concentration in the stream water is 6 mg l . The maximum
-1
nitrification rate constant at 20 °C k = 1.8 d , the temperature coefficient for
n,max,20°
-1
nitrification θ = 1.04, the Monod half-saturation concentration M = 2.0 mg l .
n n
+
Calculate the NH concentration at 2.5 km downstream from the effluent outfall
4
+
and the distance at which the NH concentration has dwindled to the level upstream
4
-1
from the outfall (0.22 mg l ). Assume instantaneous mixing and neglect dispersion .
10/1/2013 6:45:13 PM
Soil and Water.indd 262
Soil and Water.indd 262 10/1/2013 6:45:13 PM