Page 338 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 338
Patterns in groundwater 325
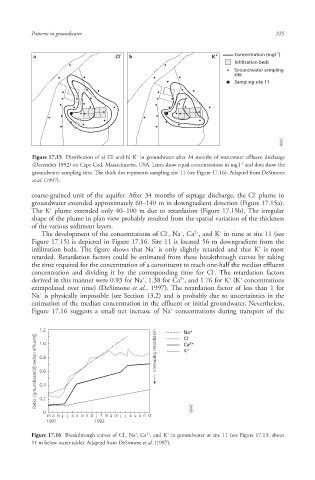
a Cl - b K + Concentration (mgl -1 )
Infiltration beds
Groundwater sampling
site
Sampling site 11
20 20 20
800
800
800
10 10 10
500
500
500
5 5 5
200
200
200
6642 6642 6642
+
-
Figure 17.15 Distribution of a) Cl and b) K in groundwater after 34 months of wastewater effluent discharge
-1
(December 1992) on Cape Cod , Massachusetts, USA. Lines show equal concentrations in mg l and dots show the
groundwater sampling sites. The thick dot represents sampling site 11 (see Figure 17.16). Adapted from DeSimone
et al. (1997).
-
coarse-grained unit of the aquifer. After 34 months of septage discharge, the Cl plume in
groundwater extended approximately 60–140 m in downgradient direction (Figure 17.15a).
+
The K plume extended only 40–100 m due to retardation (Figure 17.15b). The irregular
shape of the plume in plan view probably resulted from the spatial variation of the thickness
of the various sediment layers.
+
+
2+
-
The development of the concentrations of Cl , Na , Ca , and K in time at site 11 (see
Figure 17.15) is depicted in Figure 17.16. Site 11 is located 56 m downgradient from the
+
+
infiltration beds. The figure shows that Na is only slightly retarded and that K is most
retarded. Retardation factors could be estimated from these breakthrough curve s by taking
the time required for the concentration of a constituent to reach one-half the median effluent
-
concentration and dividing it by the corresponding time for Cl . The retardation factor s
+
+
2+
+
derived in this manner were 0.93 for Na , 1.38 for Ca , and 1.76 for K (K concentrations
extrapolated over time) (DeSimone et al., 1997). The retardation factor of less than 1 for
+
Na is physically impossible (see Section 13.2) and is probably due to uncertainties in the
estimation of the median concentration in the effluent or initial groundwater. Nevertheless,
+
Figure 17.16 suggests a small net increase of Na concentrations during transport of the
1.2 Na + - + 2+
Ratio: [groundwater]/[median effluent]] 0.8 increasing retardation K
Cl
1.0
Ca
0.6
0.4
0.2
0 6642 6642 6642
m a m j ja s o n d j f m a m j ja s o n d
1991 1992
2+
+
-
+
Figure 17.16 Breakthrough curves of Cl , Na , Ca , and K in groundwater at site 11 (see Figure 17.13; about
11 m below water table ). Adapted from DeSimone et al. (1997).
10/1/2013 6:47:06 PM
Soil and Water.indd 337
Soil and Water.indd 337 10/1/2013 6:47:06 PM