Page 363 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 363
350 Soil and Water Contamination
sediment concentration. However, due to sediment depletion, the concentration response is
often much less during the second or third hydrological event later during the year.
Asselman (1999) studied sediment concentration dynamics during 112 periods of
increased discharge in the river Rhine near Rees, Germany. She distinguished the following
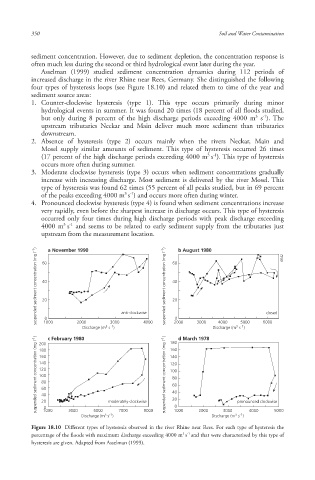
four types of hysteresis loops (see Figure 18.10) and related them to time of the year and
sediment source areas:
1. Counter-clockwise hysteresis (type 1). This type occurs primarily during minor
hydrological events in summer. It was found 20 times (18 percent of all floods studied,
3
-1
but only during 8 percent of the high discharge periods exceeding 4000 m s ). The
upstream tributaries Neckar and Main deliver much more sediment than tributaries
downstream.
2. Absence of hysteresis (type 2) occurs mainly when the rivers Neckar, Main and
Mosel supply similar amounts of sediment . This type of hysteresis occurred 26 times
3 -1
(17 percent of the high discharge periods exceeding 4000 m s ). This type of hysteresis
occurs more often during summer.
3. Moderate clockwise hysteresis (type 3) occurs when sediment concentrations gradually
increase with increasing discharge. Most sediment is delivered by the river Mosel. This
type of hysteresis was found 62 times (55 percent of all peaks studied, but in 69 percent
3 -1
of the peaks exceeding 4000 m s ) and occurs more often during winter.
4. Pronounced clockwise hysteresis (type 4) is found when sediment concentrations increase
very rapidly, even before the sharpest increase in discharge occurs. This type of hysteresis
occurred only four times during high discharge periods with peak discharge exceeding
3 -1
4000 m s and seems to be related to early sediment supply from the tributaries just
upstream from the measurement location. b August 1980 6642 6642 6642
suspended sediment concentration (mg l -1 ) 60 suspended sediment concentration (mg l -1 ) 60
a November 1990
40
40
20
20
closed
0
0
5000
1000
2000
3000
4000
4000
Discharge (m 3 s -1 ) anti-clockwise 180 2000 3000 Discharge (m 3 s -1 ) 6000
suspended sediment concentration (mg l -1 ) 160 suspended sediment concentration (mg l -1 ) 140
c February 1980
d March 1978
200
160
180
140
120
120
100
100
80
80
60
60
40
40
20
moderately-clockwise
pronounced clockwise
0
0
3000
3000
5000
1000
Discharge (m 3 s -1 ) 7000 9000 20 1000 2000 Discharge (m 3 s -1 ) 4000 5000
Figure 18.10 Different types of hysteresis observed in the river Rhine near Rees. For each type of hysteresis the
3 -1
percentage of the floods with maximum discharge exceeding 4000 m s and that were characterised by this type of
hysteresis are given. Adapted from Asselman (1999).
10/1/2013 6:47:12 PM
Soil and Water.indd 362 10/1/2013 6:47:12 PM
Soil and Water.indd 362