Page 366 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 366
Patterns in surface water 353
1000
a 6642
800
Concentration (mg/l)
b 600
THE
NETHERLANDS 400
IJssel
200
Nederrijn-Lek Rees
Rees
Waal
Lippe
GERMANY 0 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 12000
Ruhr Discharge (m 3 /s)
Kalkofen Rheinfelden
100 km Sieg Rockenau Maxau
Hauconcourt
Rhine
Worms
Lahn Kleinheubach Kaub
Andernach
Kalkofen
Andernach Kalkofen Schweinfurt Andernach
Rees
Cochem
Cochem
Cochem Kaub Schweinfurt
Schweinfurt
Mosel Main V
Vierethiereth
LUXEMBURG
Nahe Kleinheubach
Kleinheubach
Rockenau
Worms Rockenau
Saar
Jagst
FRANCE Rhine
Hauconcourt Maxau Kocher
Hauconcourt
Neckar
Boden?
Rheinfelden
Rheinfelden see
Aare AUSTRIA
Lac de Neuchatel Alpenrhine
SWITZERLAND
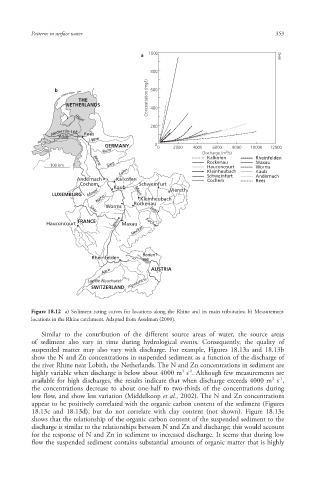
Figure 18.12 a) Sediment rating curves for locations along the Rhine and its main tributaries; b) Measurement
locations in the Rhine catchment. Adapted from Asselman (2000).
Similar to the contribution of the different source areas of water, the source areas
of sediment also vary in time during hydrological events. Consequently, the quality of
suspended matter may also vary with discharge. For example, Figures 18.13a and 18.13b
show the N and Zn concentrations in suspended sediment as a function of the discharge of
the river Rhine near Lobith, the Netherlands. The N and Zn concentrations in sediment are
3
-1
highly variable when discharge is below about 4000 m s . Although few measurements are
-1
3
available for high discharges, the results indicate that when discharge exceeds 4000 m s ,
the concentrations decrease to about one-half to two-thirds of the concentrations during
low flow, and show less variation (Middelkoop et al., 2002). The N and Zn concentrations
appear to be positively correlated with the organic carbon content of the sediment (Figures
18.13c and 18.13d), but do not correlate with clay content (not shown). Figure 18.13e
shows that the relationship of the organic carbon content of the suspended sediment to the
discharge is similar to the relationships between N and Zn and discharge; this would account
for the response of N and Zn in sediment to increased discharge. It seems that during low
flow the suspended sediment contains substantial amounts of organic matter that is highly
10/1/2013 6:47:13 PM
Soil and Water.indd 365
Soil and Water.indd 365 10/1/2013 6:47:13 PM