Page 162 - Standard Handbook Of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering
P. 162
Basic Mechanics (Statics and Dynamics) 147
W W
N 1
(a 1
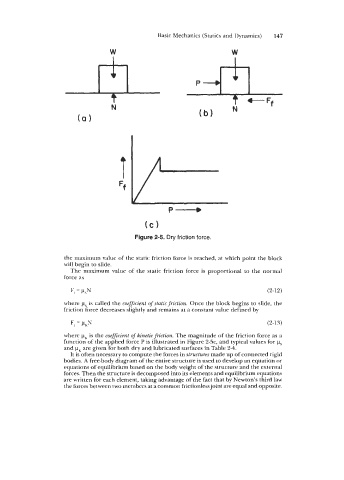
Figure 2-5. Dry friction force.
the maximum value of the static friction force is reached, at which point the block
will begin to slide.
The maximum value of the static friction force is proportional to the normal
force as
F, = psN (2-12)
where ps is called the coefficient of static friction. Once the block begins to slide, the
friction force decreases slightly and remains at a constant value defined by
F, = kL,N (2-13)
where pK is the coefficient of kinetic friction. The magnitude of the friction force as a
function of the applied force P is illustrated in Figure 2-5c, and typical values for ps
and F~ are given for both dry and lubricated surfaces in Table 2-4.
It is often necessary to compute the forces in structures made up of connected rigid
bodies. A free-body diagram of the entire structure is used to develop an equation or
equations of equilibrium based on the body weight of the structure and the external
forces. Then the structure is decomposed into its elements and equilibrium equations
are written for each element, taking advantage of the fact that by Newton’s third law
the forces between two members at a common frictionlessjoint are equal and opposite.