Page 166 - Standard Handbook Of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering
P. 166
Dynamics 151
P// '
I
1
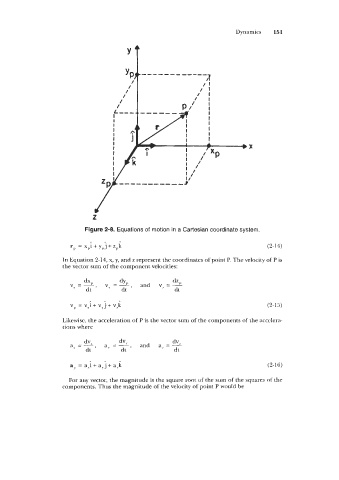
Figure 2-8. Equations of motion in a Cartesian coordinate system.
A
*
rp = xpi + y,j + z,k (2-14)
In Equation 2-14, x, y, and z represent the coordinates of point P. The velocity of P is
the vector sum of the component velocities:
* . .
v, = v,i + v, j + vzk (2-15)
Likewise, the acceleration of P is the vector sum of the components of the accelera-
tions where
- dv,
dv\
- dv,
a, - - a, = - and a, - -
dt ' dt ' dt
A *
ap = axi + a, j + a,k (2-16)
For any vector, the magnitude is the square root of the sum of the squares of the
components. Thus the magnitude of the velocity of point P would be