Page 171 - Standard Handbook Of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering
P. 171
156 General Engineering and Science
(C 1 (d)
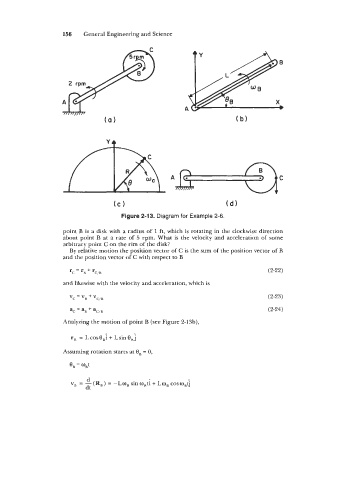
Figure 2-13. Diagram for Example 2-6.
point B is a disk with a radius of 1 ft, which is rotating in the clockwise direction
about point B at a rate of 5 rpm. What is the velocity and acceleration of some
arbitrary point C on the rim of the disk?
By relative motion the position vector of C is the sum of the position vector of B
and the position vector of C with respect to B
rC 'B -k 'C/B (2-22)
and likewise with the velocity and acceleration, which is
v, = v, + VC/, (2-23)
(2-24)
= + 'C/B
Analyzing the motion of point B (see Figure 2-13b),
rB = LcosB,i+ LsinB,j
Assuming rotation starts at 8, = 0,
8, = O,t
d
v, = -(R,) = -LO, sinO,ti + LO, COSO,~~
dt