Page 325 - Statistics for Dummies
P. 325
Chapter 19: Two-Way Tables and Independence
Comparing the results of two conditional distributions
Two categorical variables are independent if the conditional distributions
are the same for all groups being compared. The variables are independent
because breaking them down and comparing them by group doesn’t change
the results. In the election example I introduced at the beginning of “Checking
Independence and Describing Dependence,” independence means the condi-
tional distribution for opinion is the same for the males and the females.
Suppose you do a survey of 200 voters to see if gender is related to whether
they voted for the incumbent president, and you summarize your results in
Table 19-8.
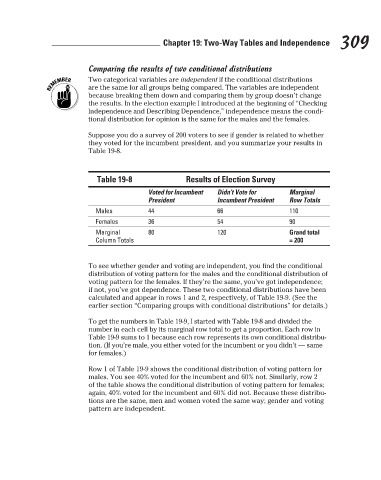
Results of Election Survey
Table 19-8
President
Row Totals
Incumbent President
66
Males Voted for Incumbent Didn’t Vote for Marginal 309
110
44
Females 36 54 90
Marginal 80 120 Grand total
Column Totals = 200
To see whether gender and voting are independent, you find the conditional
distribution of voting pattern for the males and the conditional distribution of
voting pattern for the females. If they’re the same, you’ve got independence;
if not, you’ve got dependence. These two conditional distributions have been
calculated and appear in rows 1 and 2, respectively, of Table 19-9. (See the
earlier section “Comparing groups with conditional distributions” for details.)
To get the numbers in Table 19-9, I started with Table 19-8 and divided the
number in each cell by its marginal row total to get a proportion. Each row in
Table 19-9 sums to 1 because each row represents its own conditional distribu-
tion. (If you’re male, you either voted for the incumbent or you didn’t — same
for females.)
Row 1 of Table 19-9 shows the conditional distribution of voting pattern for
males. You see 40% voted for the incumbent and 60% not. Similarly, row 2
of the table shows the conditional distribution of voting pattern for females;
again, 40% voted for the incumbent and 60% did not. Because these distribu-
tions are the same, men and women voted the same way; gender and voting
pattern are independent.
3/25/11 8:13 PM
27_9780470911082-ch19.indd 309 3/25/11 8:13 PM
27_9780470911082-ch19.indd 309