Page 100 - Synthetic Fuels Handbook
P. 100
FUELS FROM PETROLEUM AND HEAVY OIL 87
Solvent
Wash
solvent
O
Slack wax evaporator
Heater
Rotary filter
Dewaxed oil evaporator
Chiller
Heat exchanger
Steam heater Heater
Feed Dewaxed oil Stack wax
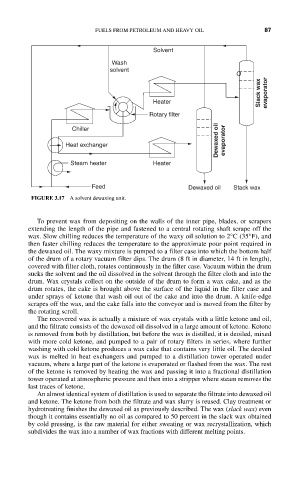
FIGURE 3.17 A solvent dewaxing unit.
To prevent wax from depositing on the walls of the inner pipe, blades, or scrapers
extending the length of the pipe and fastened to a central rotating shaft scrape off the
wax. Slow chilling reduces the temperature of the waxy oil solution to 2°C (35°F), and
then faster chilling reduces the temperature to the approximate pour point required in
the dewaxed oil. The waxy mixture is pumped to a filter case into which the bottom half
of the drum of a rotary vacuum filter dips. The drum (8 ft in diameter, 14 ft in length),
covered with filter cloth, rotates continuously in the filter case. Vacuum within the drum
sucks the solvent and the oil dissolved in the solvent through the filter cloth and into the
drum. Wax crystals collect on the outside of the drum to form a wax cake, and as the
drum rotates, the cake is brought above the surface of the liquid in the filter case and
under sprays of ketone that wash oil out of the cake and into the drum. A knife-edge
scrapes off the wax, and the cake falls into the conveyor and is moved from the filter by
the rotating scroll.
The recovered wax is actually a mixture of wax crystals with a little ketone and oil,
and the filtrate consists of the dewaxed oil dissolved in a large amount of ketone. Ketone
is removed from both by distillation, but before the wax is distilled, it is deoiled, mixed
with more cold ketone, and pumped to a pair of rotary filters in series, where further
washing with cold ketone produces a wax cake that contains very little oil. The deoiled
wax is melted in heat exchangers and pumped to a distillation tower operated under
vacuum, where a large part of the ketone is evaporated or flashed from the wax. The rest
of the ketone is removed by heating the wax and passing it into a fractional distillation
tower operated at atmospheric pressure and then into a stripper where steam removes the
last traces of ketone.
An almost identical system of distillation is used to separate the filtrate into dewaxed oil
and ketone. The ketone from both the filtrate and wax slurry is reused. Clay treatment or
hydrotreating finishes the dewaxed oil as previously described. The wax (slack wax) even
though it contains essentially no oil as compared to 50 percent in the slack wax obtained
by cold pressing, is the raw material for either sweating or wax recrystallization, which
subdivides the wax into a number of wax fractions with different melting points.