Page 99 - Synthetic Fuels Handbook
P. 99
86 CHAPTER THREE
Solvent
to
recovery
Steam Steam
Steam
Condensate
Deasphalter
charge Solvent
Deasphalter to
recovery
Solvent
stripper
Steam
Recovered
solvent
Deasphalted
oil
To asphalt
recovery
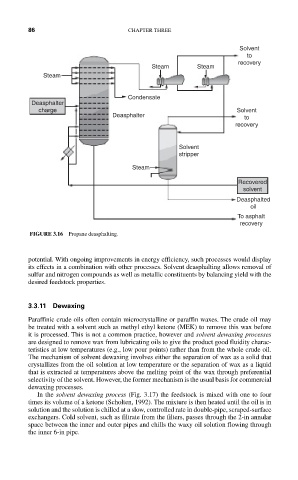
FIGURE 3.16 Propane deasphalting.
potential. With ongoing improvements in energy efficiency, such processes would display
its effects in a combination with other processes. Solvent deasphalting allows removal of
sulfur and nitrogen compounds as well as metallic constituents by balancing yield with the
desired feedstock properties.
3.3.11 Dewaxing
Paraffinic crude oils often contain microcrystalline or paraffin waxes. The crude oil may
be treated with a solvent such as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) to remove this wax before
it is processed. This is not a common practice, however and solvent dewaxing processes
are designed to remove wax from lubricating oils to give the product good fluidity charac-
teristics at low temperatures (e.g., low pour points) rather than from the whole crude oil.
The mechanism of solvent dewaxing involves either the separation of wax as a solid that
crystallizes from the oil solution at low temperature or the separation of wax as a liquid
that is extracted at temperatures above the melting point of the wax through preferential
selectivity of the solvent. However, the former mechanism is the usual basis for commercial
dewaxing processes.
In the solvent dewaxing process (Fig. 3.17) the feedstock is mixed with one to four
times its volume of a ketone (Scholten, 1992). The mixture is then heated until the oil is in
solution and the solution is chilled at a slow, controlled rate in double-pipe, scraped-surface
exchangers. Cold solvent, such as filtrate from the filters, passes through the 2-in annular
space between the inner and outer pipes and chills the waxy oil solution flowing through
the inner 6-in pipe.