Page 70 - TPM A Route to World-Class Performance
P. 70
The top-down and bottom-up realities of TPM 51
cause problems which can be prevented (the four Ps) because they are to do
with materials, machines, mechanisms and manpower (the four Ms).
This is the acid test of the TPM pilot@) since the teams are trained, encouraged
and motivated to resolve (once and for all) the six losses which work against
the achievement of world-class levels of overall equipment effectiveness.
These problem-solving opportunities can usually be classified as:
0 operational problems/improvements involving no cost or low cost and
low risk solutions;
technical problems/improvements, often involving the key contacts and
also some cost and, hence, risk;
0 support services and/or support equipment problems/improvements
which can involve the key contacts and some low cost but low risk.
Obviously the elimination of problems needs to be developed into the best
practice routines, the impact of which will feed back into an improved OEE
figure.
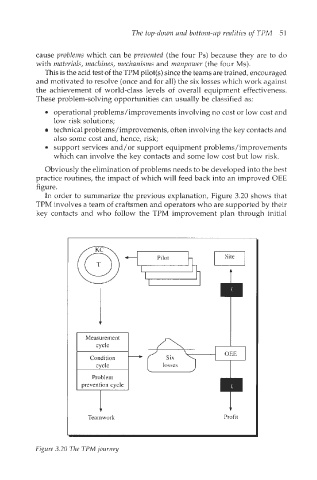
In order to summarize the previous explanation, Figure 3.20 shows that
TPM involves a team of craftsmen and operators who are supported by their
key contacts and who follow the TPM improvement plan through initial
t
U
Site
Measurement
OEE
Condition Six
losses
Problem
Teamwork Profit
Figure 3.20 The TPM journey