Page 200 - The Six Sigma Project Planner
P. 200
efforts. For our example, Internet connectivity obviously has a huge customer impact.
‘Easy to use quickly after I’ve learned it’ has relatively low impact. ‘Easy to learn’ is
dominated by one item: the user interface. These weights will be used to assess different
proposed upgrade designs and plans.
Each plan will be evaluated on each subcategory item and assigned a value depending
on how well it addresses the item. The values will be multiplied by the global weights
to arrive at an overall score for the plan. The scores can be rank-ordered to provide a list
that the process owner can use when making resource allocation decisions. Or, more
proactively, the information can be used to develop a plan that emphasizes the most
important customer demands.
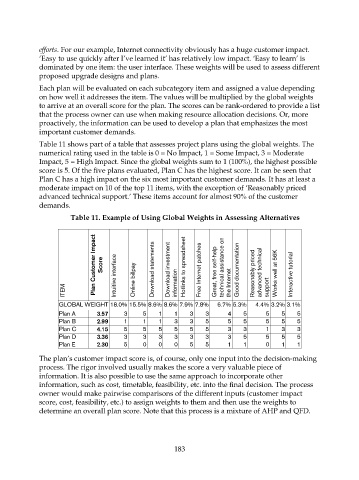
Table 11 shows part of a table that assesses project plans using the global weights. The
numerical rating used in the table is 0 = No Impact, 1 = Some Impact, 3 = Moderate
Impact, 5 = High Impact. Since the global weights sum to 1 (100%), the highest possible
score is 5. Of the five plans evaluated, Plan C has the highest score. It can be seen that
Plan C has a high impact on the six most important customer demands. It has at least a
moderate impact on 10 of the top 11 items, with the exception of ‘Reasonably priced
advanced technical support.’ These items account for almost 90% of the customer
demands.
Table 11. Example of Using Global Weights in Assessing Alternatives
Plan Customer Impact Score Intuitive interface Download statements Download investment Hotlinks to spreadsheet Free Internet patches Great, free self-help technical assistance on Good documentation Reasonably priced advanced technical Works well at 56K Interactive tutorial
ITEM Online billpay information the Internet support
GLOBAL WEIGHT 18.0% 15.5% 8.6% 8.6% 7.9% 7.8% 6.7% 5.3% 4.4% 3.2% 3.1%
Plan A 3.57 3 5 1 1 3 3 4 5 5 5 5
Plan B 2.99 1 1 1 3 3 5 5 5 5 5 5
Plan C 4.15 5 5 5 5 5 5 3 3 1 3 3
Plan D 3.36 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 5 5 5 5
Plan E 2.30 5 0 0 0 5 5 1 1 0 1 1
The plan’s customer impact score is, of course, only one input into the decision-making
process. The rigor involved usually makes the score a very valuable piece of
information. It is also possible to use the same approach to incorporate other
information, such as cost, timetable, feasibility, etc. into the final decision. The process
owner would make pairwise comparisons of the different inputs (customer impact
score, cost, feasibility, etc.) to assign weights to them and then use the weights to
determine an overall plan score. Note that this process is a mixture of AHP and QFD.
183