Page 55 - The Six Sigma Project Planner
P. 55
A common problem to guard against is scope creep. As activities are developed, be
certain that they do not go beyond the project’s original scope. Equally common is the
problem of scope drift. In these cases, the project focus gradually moves away from its
original charter. Since the activities are the project, this is a good place to carefully
review the scope statement in the project charter (p. 2) to ensure that the project remains
focused on its goals and objectives.
Activity Dependencies
Some project activities depend on others: sometimes a given activity may not begin
until another activity is complete. For example, if the project involves building a house,
the construction of the floor cannot begin until the foundation has been poured and had
time to cure properly. Other activities can be done in parallel, simultaneously. The
outside of the house can be painted while the drywall is being installed inside or while
the roof shingles are being installed. The project plan and schedule must take these
dependencies into account.
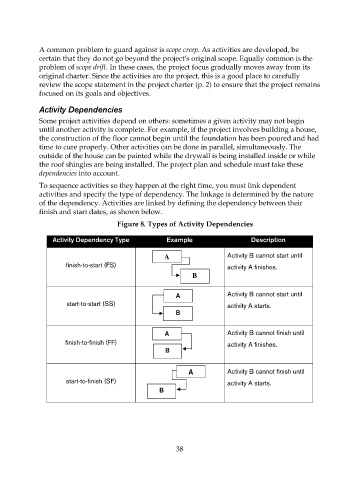
To sequence activities so they happen at the right time, you must link dependent
activities and specify the type of dependency. The linkage is determined by the nature
of the dependency. Activities are linked by defining the dependency between their
finish and start dates, as shown below.
Figure 8. Types of Activity Dependencies
Activity Dependency Type Example Description
A Activity B cannot start until
finish-to-start (FS) activity A finishes.
B
A Activity B cannot start until
start-to-start (SS) activity A starts.
B
A Activity B cannot finish until
finish-to-finish (FF) activity A finishes.
B
A Activity B cannot finish until
start-to-finish (SF) activity A starts.
B
38