Page 113 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 113
AI9 Gas bearinas
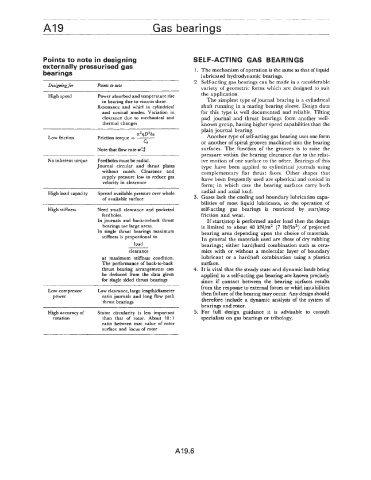
Points to note in designing SELF-ACTING GAS BEARINGS
externally pressurised gas
bearings 1. The mechanism of operation is the same as that of liquid
lubricated hydrodynamic bearings.
2. Self-acting gas bearings can be made in a considerable
Desigaing for Points to note
variety of geometric forms which are designed to suit
High speed Power absorbed and temperature rise the application.
in bearing due to viscous shear. The simplest type of journal bearing is a cylindrical
Resonance and whirl in cylindrical shaft running in a mating bearing sleeve. Design data
and conical modes. Variation in for this type is well documented and reliable. Tilting
clearance due to mechanical and pad journal and thrust bearings form another well-
thermal changes known group, having higher speed capabilities than the
plain journal bearing.
z2qD3bn
Low friction Friction torque = - Another type of self-acting gas bearing uses one form
cd or another of spiral grooves machined into the bearing
Note that flow rate aCj surfaces. The function of the grooves is to raise the
pressure within the bearing clearance due to the relat-
No inherent torque Feedholes must be radial. ive motion of one surface to the other. Bearings of this
Journal circular and thrust plates type have been applied to cylindrical journals using
without swash. Clearance and complementary flat thrust faces. Other shapes that
supply pressure low to reduce gas have been frequently used are spherical and conical in
velocity in clearance
form; in which case the bearing surfaces carry both
High load capacity Spread available pressure over whole radial and axial load.
of available surface 3. Gases lack the cooling and boundary lubrication capa-
bilities of most liquid lubricants, so the operation of
~~
High stiffness Need small clearance and pocketed self-acting gas bearings is restricted by start/stop
feedholes. friction and wear.
In journals and back-to-back thrust If startlstop is performed under load then the design
bearings use large areas. is limited to about 48 kN/m2 (7 lbf/in2) of projected
In single thrust bearings maximum bearing area depending upon the choice of materials.
stiffness is proportional to In general the materials used are those of dry rubbing
load bearings; either hard/hard combination such as cera-
clearance mics with or without a molecular layer of boundary
at maximum stiffness condition. lubricant or a hard/soft combination using a plastics
The performance of back-to-back surface.
thrust bearing arrangements can 4. It is vital that the steady state and dynamic loads being
be deduced from the data given applied to a self-acting gas bearing are known precisely
for single sided thrust bearings since if contact between the bearing surfaces results
from the response to external forces or whirl instabilities
Low compressor Low clearance, large length/diameter then failure of the bearing may occur. Any design should
power ratio journals and long flow path
thrust bearings therefore include a dynamic analysis of the system of
bearings and rotor.
High accuracy of Stator circularity is less important 5. For full design guidance it is advisable to consult
rotation than that of rotor. About 10: 1 specialists on gas bearings or tribology.
ratio between mzc value of rotor
surface and locus of rotor
A19.6