Page 271 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 271
B22 Labyrinths, brush seals and throttling bushes
VISCOSEAL
(Also called a screw seal or wind back seal)
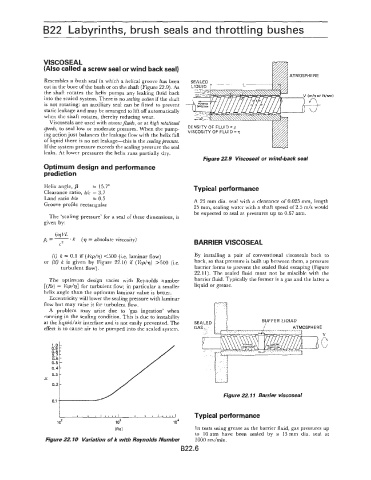
Resembles a bush seal in which a helical groove has been SEALED
L
cut in the bore of the bush or on the shaft (Figure 22.9). As LIQUID r-p
the shaft rotates the helix pumps any leaking fluid back (m/s or ft/sec)
into the sealed system. There is no sealing action if the shaft
is not rotating: an auxiliary seal can be fitted to prevent 3-
static leakage and may be arranged to lift off automatically
when the shaft rotates, thereby reducing wear.
Viscoseals are used with ViscousJuids, or at high rotational
speeds, to seal low or moderate presures. When the pump- DENSITY OF FLUID = p
VISCOSITY OF FLUID = q
ing action just balances the leakage flow with the helix full
of liquid there is no net leakage-this is the sealing pressure.
If the system pressure exceeds the sealing pressure the seal
leaks. At lower pressures the helix runs partially dry.
Figure 22.9 Viscoseal or wind-back seal
Optimum design and performance
prediction
Helix angle, p = 15.7" Typical performance
Clearance ratio, h/c = 3.7
Land ratio b/a = 0.5 A 25 mm dia. seal with a clearance of 0.025 mm, length
Groove profile rectangular 25 mm, sealing water with a shaft speed of 2.5 m/s would
be expected to seal at pressures up to 0.67 atm.
The 'sealing pressure' for a seal of these dimensions, is
given by:
671 VL
PI=-. k (71 = absolute viscosity)
2 BARRIER VISCOSEAL
(i) k = 0.1 if (Vcp/q) <500 (Le. laminar flow) By installing a pair of conventional viscoseals back to
or (ii) k is given by Figure 22.10 if (Vcplq) >500 (Le. back, so that pressure is built up between them, a pressure
turbulent flow). barrier forms to prevent the sealed fluid escaping (Figure
22.11). The sealed fluid must not be miscible with the
The optimum design varies with Reynolds number barrier fluid. Typically the former is a gas and the latter a
[(Re) = Vcp/71] for turbulent flow; in particular a smaller liquid or grease.
helix angle than the optimum laminar value is better.
Eccentricity will lower the sealing pressure with laminar
flow but may raise it for turbulent flow.
A problem may arise due to 'gas ingestion' when
running in the sealing condition. This is due to instability
at the liquid/air interface and is not easily prevented. The BUFFER LIQUID
effect is to cause air to be pumped into the sealed system.
Y
Figure 22.11 Barrier viscoseal
I I I I III I I I I n n m J Typical performance
lo2 103 10'
In tests using grease as the barrier fluid, gas pressures up
(Re)
to 10 atm have been sealed by a 13 mm dia. seal at
Figure 22.10 Variation of k with Reynolds Number 1000 rev/min.
B22.6