Page 192 - Welding of Aluminium and its Alloys
P. 192
Resistance welding processes 175
surface indentation can be readily identified. These features may be used
to assess the quality of production batches.
9.5 Seam welding
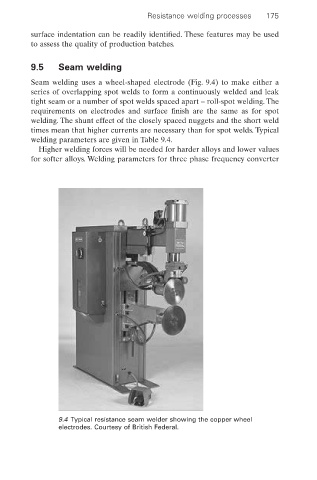
Seam welding uses a wheel-shaped electrode (Fig. 9.4) to make either a
series of overlapping spot welds to form a continuously welded and leak
tight seam or a number of spot welds spaced apart – roll-spot welding. The
requirements on electrodes and surface finish are the same as for spot
welding. The shunt effect of the closely spaced nuggets and the short weld
times mean that higher currents are necessary than for spot welds. Typical
welding parameters are given in Table 9.4.
Higher welding forces will be needed for harder alloys and lower values
for softer alloys. Welding parameters for three phase frequency converter
9.4 Typical resistance seam welder showing the copper wheel
electrodes. Courtesy of British Federal.