Page 1046 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 1046
a
a a 0 1
(a) (b) (c)
a
a a
0 1 0 1
0 1
(d) (e)
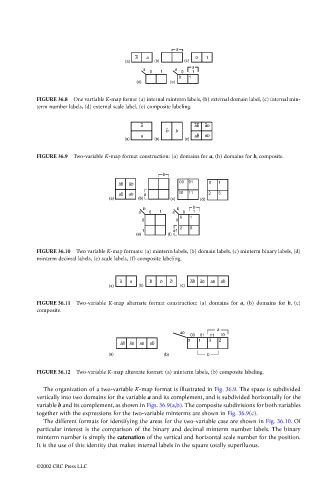
FIGURE 36.8 One vartiable K-map forms: (a) internal minterm labels, (b) external domain label, (c) internal min-
term number labels, (d) external scale label, (e) composite labeling.
a ab ab
b b
a ab ab
(a) (b) (c)
FIGURE 36.9 Two-variable K-map format construction: (a) domains for a, (b) domains for b, composite.
b
00 01 0 1
ab ab
10 11 2 3
ab ab a
(a) (b) (c) (d)
b b b
a 0 1 a 0 1
0 1
0 0
2 3
1 a 1
(e) (f)
FIGURE 36.10 Two variable K-map formats: (a) minterm labels, (b) domain labels, (c) minterm binary labels, (d)
minterm decimal labels, (e) scale labels, (f) composite labeling.
a a b b b ab ab ab ab
(a) (b) (c)
FIGURE 36.11 Two-variable K-map alternate format construction: (a) domains for a, (b) domains for b, (c)
composite.
a
ab
00 01 11 10
0 1 3 2
ab ab ab ab
(a) (b) b
FIGURE 36.12 Two-variable K-map alternate format: (a) minterm labels, (b) composite labeling.
The organization of a two-variable K-map format is illustrated in Fig. 36.9. The space is subdivided
vertically into two domains for the variable a and its complement, and is subdivided horizontally for the
variable b and its complement, as shown in Figs. 36.9(a,b). The composite subdivisions for both variables
together with the expressions for the two-variable minterms are shown in Fig. 36.9(c).
The different formats for identifying the areas for the two-variable case are shown in Fig. 36.10. Of
particular interest is the comparison of the binary and decimal minterm number labels. The binary
minterm number is simply the catenation of the vertical and horizontal scale number for the position.
It is the use of this identity that makes internal labels in the square totally superfluous.
©2002 CRC Press LLC