Page 1041 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 1041
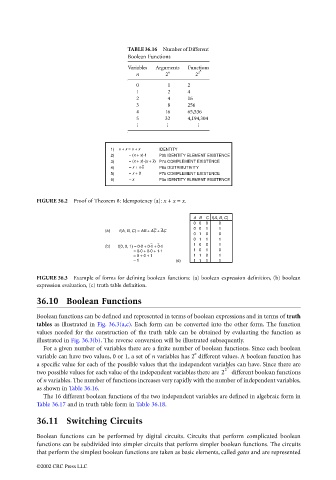
TABLE 36.16 Number of Different
Boolean Functions
Variables Arguments Functions
n
n 2 n 2 2
‘
0 1 2
1 2 4
2 4 16
3 8 256
4 16 65,536
5 32 4,194,304
‘
1) x + x = x + x IDENTITY
2) = (x + x) . 1 P3b IDENTITY ELEMENT EXISTENCE
3) = (x + x) . (x + x) P7a COMPLEMENT EXISTENCE
4) = x + x . x P6a DISTRIBUTIVITY
5) = x + 0 P7b COMPLEMENT EXISTENCE
6) = x P3a IDENTITY ELEMENT EXISTENCE
FIGURE 36.2 Proof of Theorem 8: Idempotency (a): x + x = x.
A B C f(A, B, C)
0 0 0 0
0 0 1 1
(a) f(A, B, C) = AB + AC + AC
0 1 0 0
0 1 1 1
1 0 0 1
(b) f(0, 0, 1) = 0 . 0 + 0 . 1 + 0 . 1
= 0 . 0 + 0 . 0 + 1 . 1 1 0 1 0
= 0 + 0 + 1 1 1 0 1
= 1 (c) 1 1 1 1
FIGURE 36.3 Example of forms for defining boolean functions: (a) boolean expression definition, (b) boolean
expression evaluation, (c) truth table definition.
36.10 Boolean Functions
Boolean functions can be defined and represented in terms of boolean expressions and in terms of truth
tables as illustrated in Fig. 36.3(a,c). Each form can be converted into the other form. The function
values needed for the construction of the truth table can be obtained by evaluating the function as
illustrated in Fig. 36.3(b). The reverse conversion will be illustrated subsequently.
For a given number of variables there are a finite number of boolean functions. Since each boolean
n
variable can have two values, 0 or 1, a set of n variables has 2 different values. A boolean function has
a specific value for each of the possible values that the independent variables can have. Since there are
n
two possible values for each value of the independent variables there are 2 2 different boolean functions
of n variables. The number of functions increases very rapidly with the number of independent variables,
as shown in Table 36.16.
The 16 different boolean functions of the two independent variables are defined in algebraic form in
Table 36.17 and in truth table form in Table 36.18.
36.11 Switching Circuits
Boolean functions can be performed by digital circuits. Circuits that perform complicated boolean
functions can be subdivided into simpler circuits that perform simpler boolean functions. The circuits
that perform the simplest boolean functions are taken as basic elements, called gates and are represented
©2002 CRC Press LLC