Page 122 - Theory and Design of Air Cushion Craft
P. 122
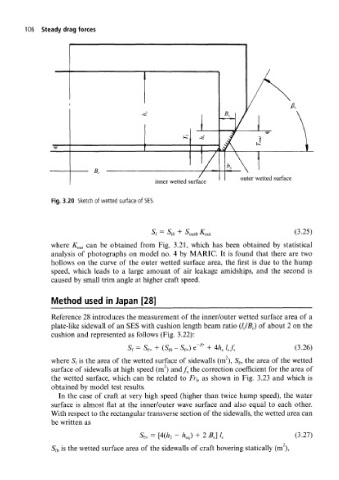
106 Steady drag forces
outer wetted surface
inner wetted surface
Fig. 3.20 Sketch of wetted surface of SES.
o I o js /"2 TC\
f ^iO ' ^outO -*^out \J.£J)
where K out can be obtained from Fig. 3.21, which has been obtained by statistical
analysis of photographs on model no. 4 by MARIC. It is found that there are two
hollows on the curve of the outer wetted surface area, the first is due to the hump
speed, which leads to a large amount of air leakage amidships, and the second is
caused by small trim angle at higher craft speed.
Method used in Japan [28]
Reference 28 introduces the measurement of the inner/outer wetted surface area of a
plate-like sidewall of an SES with cushion length beam ratio (IJB C) of about 2 on the
cushion and represented as follows (Fig. 3.22):
Fr
S = S + (S — S~) e~ + 4h I f (3.26)
where S f is the area of the wetted surface of sidewalls (m ), S f30 the area of the wetted
2
surface of sidewalls at high speed (m ) and/ s the correction coefficient for the area of
the wetted surface, which can be related to Fr,, as shown in Fig. 3.23 and which is
obtained by model test results.
In the case of craft at very high speed (higher than twice hump speed), the water
surface is almost flat at the inner/outer wave surface and also equal to each other.
With respect to the rectangular transverse section of the sidewalls, the wetted area can
be written as
S*. = [4(A 2 - A eq) + 2 B,] /, (3.27)
S m is the wetted surface area of the sidewalls of craft hovering statically (m ),